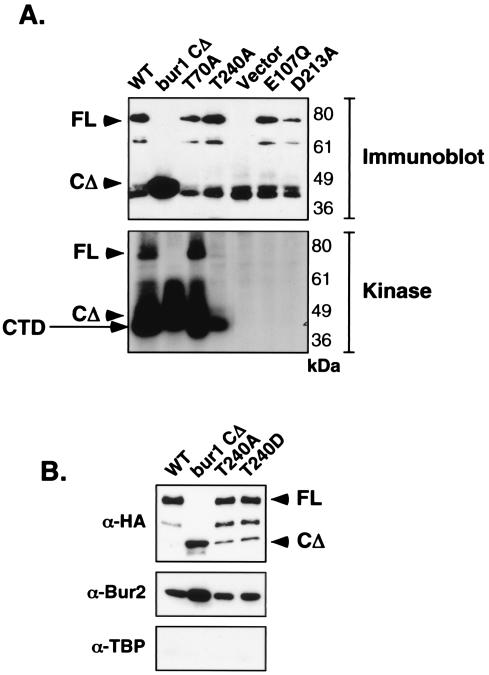
FIG. 3.
In vitro CTD kinase activity of Bur1 mutant alleles. (A) Plasmids expressing epitope-tagged Bur1 mutants were transformed into YSB787 containing an untagged wild-type Bur1. Note that plasmid shuffling was not performed here, since the E107Q and D213A alleles are unable to support growth. Tagged Bur1-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated with 12CA5-protein A beads and split. In the upper panel, the precipitates were immunoblotted with anti-HA (12CA5) antibody. FL, the full-length protein; CΔ, the C-terminal truncation protein. Note that the immunoglobulin heavy chain migrates very closely to the Bur1 CΔ mutant, giving a background band. The other aliquots of the immunoprecipitates were tested for kinase activity with radiolabeled ATP and an HA-CTD fusion protein (see Materials and Methods). The lower panel shows SDS-PAGE of the reaction mixture exposed for autoradiography, showing both CTD phosphorylation and autophosphorylation of Bur1. Note that the Bur1 CΔ protein runs near the CTD substrate. Bur1 CΔ protein autophosphorylation was confirmed in reactions lacking the CTD substrate. (B) Immunoprecipitates were prepared as described for panel A. Blots were probed with anti-HA (12CA5) antibody to identify Bur1, anti-Bur2 (generously provided by Greg Prelich), or anti-TBP as a negative control.