Figure 1.
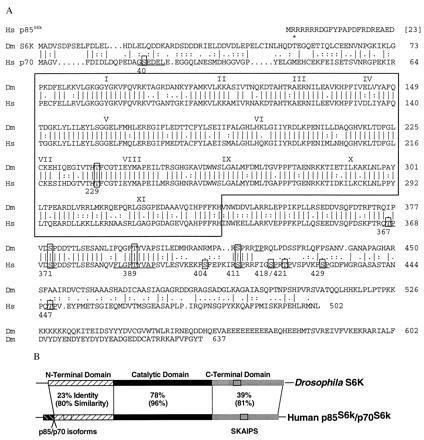
Predicted amino acid sequence of Drosophila melanogaster S6K and its alignment with human p85S6k/p70S6k. (A) Residue identities (vertical line) and conservative substitutions (:.) between S6K (Dm S6K) and p70S6k (Hs p85S6k/p70S6k) (5) are shown, with gaps introduced to maximize the alignment. Numeration of the protein sequences starts with the first in-frame methionine of S6K and the p70S6k isoform. The catalytic domain is outlined and subdomains are indicated with Roman numerals. Residues known to be phosphorylated in the mammalian protein (24) are numbered below the line and boxed with the consensus kinase recognition motif underlined adjacent to each phosphoresidue. Comparable residues conserved in Drosophila S6K are boxed and/or underlined. S6K contains the sequence motif FXGFT389YVAP that is found in members of the second messenger AGC family of related kinases (24). The pseudosubstrate autoinhibitory (SKAIPS) domain includes residues 400–424 of p70S6k (5) and the SKAIPS region in Drosophila S6K is represented by residues 409–431. The point of divergence of the putative S6K isoform is indicated above the sequence with an asterisk. Dm S6K accession no., U67304U67304; Hs p85S6k/p70S6k accession no., M60724M60724. (B) Comparisons between S6K and p70S6k showing the overall identities and similarities in the N-terminal, catalytic, and C-terminal domains. Clear box shows the location of the SKAIPS domain, and the p85S6k/p70S6k isoforms are indicated.
