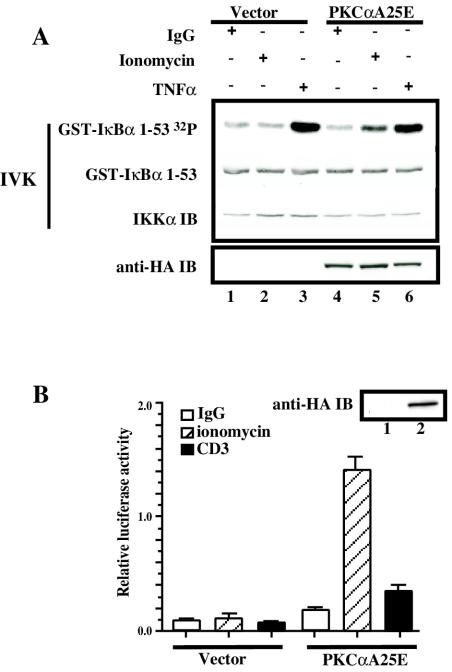
FIG. 3.
Catalytically active PKCα (PKCαA25E) activates the IKK complex and NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity. (A) Jurkat T cells (10 × 106 per sample) were electroporated with 20 μg of catalytically active PKCα (pEF-BOS/HA-PKCαA25E) (lanes 4 to 6) or control vector pEF-BOS (lanes 1 to 3). Twenty hours later, transfected Jurkat T cells were treated with 3.5-μg/ml ionomycin (lanes 2 and 5) or were stimulated with TNF (lanes 3 and 6). IKK activity was measured in an IVK assay as described above. Expression of HA-PKCαA25E was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies (anti-HA IB). (B) Jurkat T cells (10 × 106 per sample) were electroporated with 20 μg of catalytically active PKCα (pEF-BOS/HA-PKCαA25E) (lane 2) or control vector pEF-BOS (lane1) together with the reporter κB-luc (3.8 μg) and Tk-Renilla (0.2 μg) plasmids. Twenty hours later, transfected Jurkat T cells were treated with 3.5-μg/ml ionomycin or were stimulated with OKT3 monoclonal antibody (5 μg/ml). Four hours later, luciferase activity was measured and normalized as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. Expression of HA-PKCαA25E was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies (anti-HA IB). All experiments were performed in duplicate.