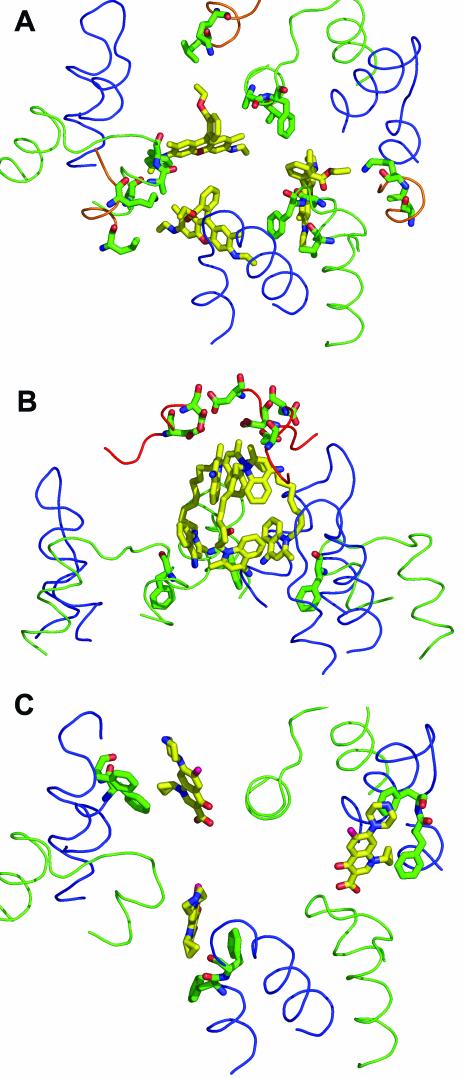
FIG. 3.
Details of the substrate-binding interactions in AcrB. The ligand is shown as a yellow stick model, and the interacting amino acid side chains (within 6 Å of the ligand molecule) are shown as green stick models. The loop between transmembrane helices 3 and 4 (residues 380 to 401) is shown as a green line, and the loop between transmembrane helices 5 and 6 (residues 452 to 475) is shown as a blue line. (A) Binding of rhodamine 6G (from PDB file 1OY8). The ligand interacts mainly with Phe386, Val382, and Ala385. The additional participation of Leu25 and Lys29 in the loop between the transmembrane helix 1 and the periplasmic domain (residues 24 to 31) (shown as an orange line) is also seen. (B) Binding of dequalinium (PDB file 1OYD). The quinolinium moiety at the top interacts with Asp99 and Asp101 from the periplasmic domain. There are no amino acid residues within the 6-Å radius of the lower quinolinium moiety. Phe386, which is 6.3 Å away, is shown. (C) Binding of ciprofloxacin (PDB file 1OYF). The ligand interacts mainly with Phe458 and Phe459, as shown. For simplicity, Leu25, Lys29, and Ala385, which are also nearby (44), are not shown here. This figure was drawn with the program PyMOL.