Figure 5.
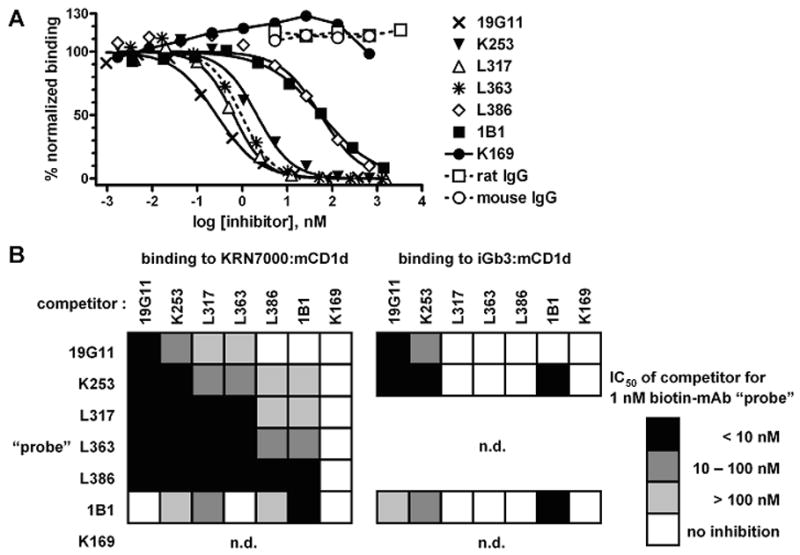
Inhibition of mAb binding to KRN7000:mCD1d by other mCD1d-reactive mAbs. (A) 1 nM mAb L363-biotin (“probe”) was allowed to bind to platebound KRN7000:mCD1d in the presence of increasing concentrations of various unlabeled mAbs. Purified total rat and mouse IgG were included as negative controls. Probe binding was revealed with AP-streptavidin, and signal was normalized as in Fig. 4. Where applicable, 4-parameter sigmoidal dose/response curves were drawn against the 0% and 100% asymptotes. The dotted curve represents inhibition of L363-biotin by “cold” L363. (B) checkerboard summary of inhibition of mAb-biotin probe binding to KRN7000:mCD1d or iGb3:mCD1d, by co-incubation with seven different mAbs. Inhibition was estimated by the concentration of mAb required for half-maximal inhibition (IC50). Darker-filled boxes indicate more potent inhibition. n.d., not done: K169-biotin was not included, since biotinylation of this mAb abolished specific binding (data not shown). Also, mAbs L317, L363 and L386 did not bind iGb3:mCD1d, so these were not included as probes in the analysis of binding to that complex.
