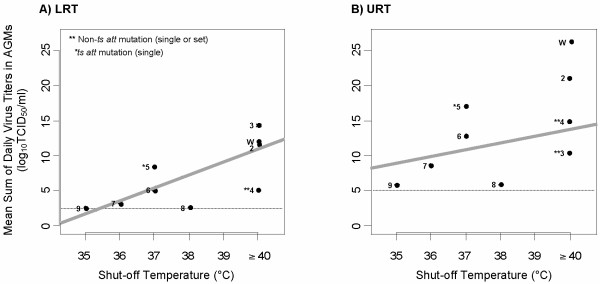
Figure 2.
Representation of the association between the in vitro shut-off temperature and the attenuation phenotype in AGMs for HPIV1 wt (W) and rHPIV1 mutant viruses. For each virus (number designations correspond to the virus group numbers assigned in tables 2-4), the shut-off temperature (°C), as determined by an in vitro temperature sensitivity assay (Table 2), was plotted against the mean sum of daily virus titers (log10 TCID50/ml; Table 3) in the URT (A) and LRT (B) of AGMs. rHPIV1 wt and non-ts rHPIV1 mutants were assigned a shut-off temperature of 40°C for the purposes of this schematic. The limit of detection for the mean sum of daily virus titers is shown by a dashed line and viruses containing a single or set of non-ts attenuating mutation (**) or a single ts attenuating mutation (*) are highlighted, as shown. A linear trend line fit using the individual daily data is shown (solid line). The Spearman rank-correlation coefficient was determined to be 0.47 for the URT and 0.67 for the LRT, indicating a moderate positive correlation between shut-off temperature and mean daily sum of virus titer in the URT and a stronger association for the LRT.