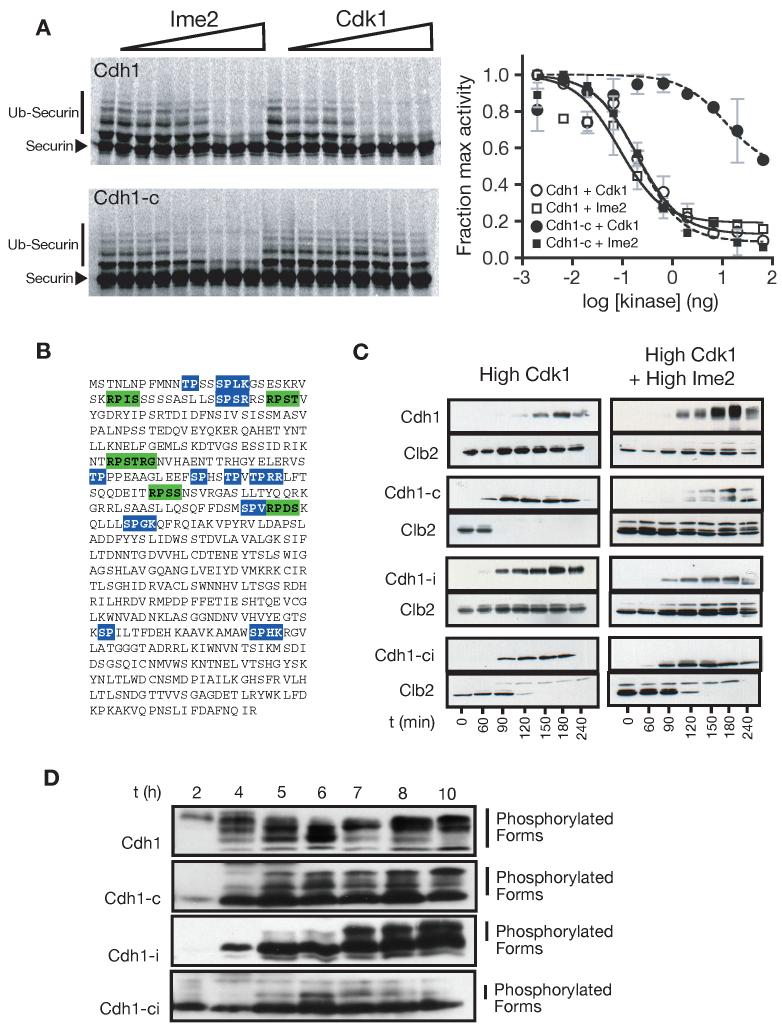
Figure 3.
Functional comparison of Ime2- and Cdk1-dependent phosphates
(A) Ime2 inhibits Cdh1 by phosphorylating non-Cdk1 sites. The ability of Cdk1 and Ime2 to inhibit Cdh1 was tested by monitoring 35S-securin ubiquitination in a reconstituted APCCdh1 assay (SDS-PAGE and autoradiography on the left, quantitation on the right. Slower migrating bands correspond to ubiquitinated securin. Data are represented as mean +/- SD). Reactions were performed with wild-type Cdh1 (top left) or Cdh1-c, in which the eleven Cdk1 sites are changed to alanine (bottom left).
(B) The primary sequence of Cdh1, showing the 11 consensus Cdk1 sites (blue) and 5 consensus Ime2 sites (green).
(C) Cdk1 and Ime2 inhibit Cdh1 using distinct phosphorylation sites in vivo. Cells were arrested in mitosis with nocodazole, and different forms of CDH1 were expressed under the control of the GAL-L promoter, in the presence or absence of Ime2. Cdh1 phosphorylation is indicated by slower migrating forms on HA3-Cdh1 western blots. APC activity was assessed by the degradation of Clb2. In addition to wild-type Cdh1, we tested mutant Cdh1 proteins lacking the 11 Cdk1 sites (Cdh1-c), lacking the five Ime2 sites (Cdh1-i), or lacking all Cdk1 and Ime2 sites (Cdh1-ic).
(D) Cdh1 is phosphorylated on both Cdk1 and Ime2 sites during meiosis. Two hours after transfer to sporulation media, wild-type and mutant forms of Cdh1 were exogenously expressed from the GAL-L promoter using the Gal4-ER system (Benjamin et al., 2003). Cdh1 mobility was monitored during meiosis by western blotting against an N-terminal HA3 tag. Time in sporulation media is indicated.