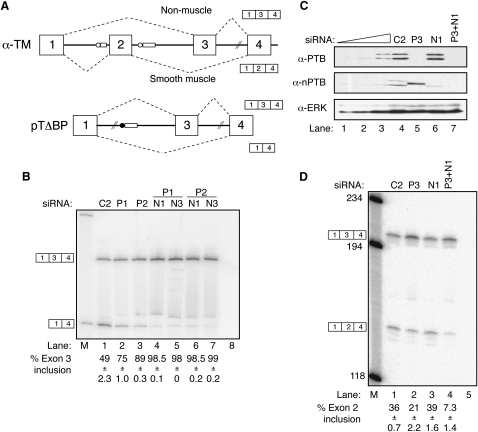
Figure 5.
PTB/nPTB Knockdown Decreases α-TM Exon 3 Skipping
(A) Schematic representation of α-TM mutually exclusive splicing (top) and pTΔBP construct (below). Exon 3 is included by default in nonmuscle cells. Exon 2 is included in smooth muscle due to repression of exon 3 by PTB. The black circle indicates the point mutations in the exon 3 branchpoint that allow detection of exon skipping in HeLa cells. Crosshatched lines indicate sequences deleted in the construct, including exon 2.
(B) RT-PCR analysis of pTΔBP alternative splicing in HeLa cells after RNAi with control C2 siRNA (lane 1) or with siRNAs against PTB (lanes 2 and 3, P1 and P2) or PTB+nPTB (lanes 4–7). Lane 8, PCR negative control. Lane M, size markers (603 and 310 nt shown). Amplicons shown schematically to the left are 435 and 309 nt. All error bars are mean ± SD, n = 3.
(C) Western blot probed for PTB (top panel), nPTB (middle panel), or ERK (bottom panel). Lanes 4–7 contain an equivalent amount of protein after RNAi in rat PAC1 cells with negative control C2 siRNA (lane 4) or with rat-specific siRNAs against PTB (lane 5), nPTB (lane 6), or PTB+nPTB (lane 7). Lanes 3, 2, and 1 contain progressive 2-fold dilutions of the C2 control sample to allow the degree of knockdown to be estimated.
(D) RT-PCR analysis of endogenous α-TM alternative splicing in RNA samples harvested from rat PAC1 cells after RNAi with negative control C2 siRNA (lane 1) or with siRNAs against PTB (lane 2), nPTB (lane 3), or PTB+nPTB (lane 4). Lane 5, PCR negative control. Samples were digested with XhoI after PCR. 1-3-4 product 194 nt, 1-2-4 product 145 nt. Numbers to the left indicate the size markers in lane M. All error bars are mean ± SD, n = 3.