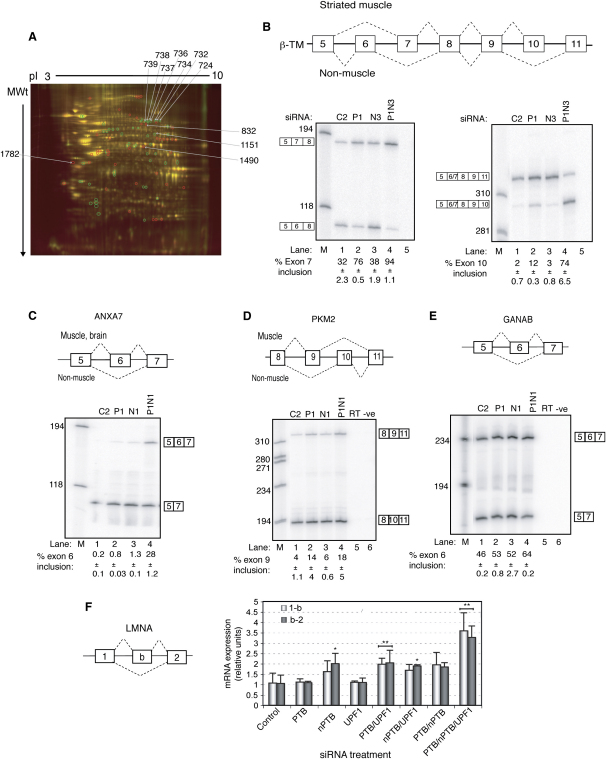
Figure 6.
Proteomic Identification of PTB Targets
(A) Representative 2D gel from the Biological Variance Analysis. The gel was loaded with 100 μg of protein from each of the Cy2 internal standard, Cy3 control, and Cy5 PTB+nPTB knockdown. Up- and downregulated spots, identified by analysis of the six gels, are indicated by red and green circles, respectively. Numbered spots correspond to proteins resulting from alterations in alternative splicing. Note that the gel is imaged in all three channels, so consistently up or downregulated spots may not appear red or green.
(B–E) RT-PCR validation of PTB/nPTB-regulated alternative splicing events in the TPM2, ANXA7, PKM2, and GANAB genes. In each case, a schematic cartoon of the alternative splicing event is shown at the top. RNA samples were harvested from HeLa cells after RNAi with control (C2, lane1), PTB (P1, lane 2), nPTB (N1, lane 3), or PTB+nPTB (P1N1, lane 4) siRNAs. Numbers to the left are size markers in lane M. All error bars are mean ± SD, n = 3.
(F) Schematic representation of LMNA alternative splicing in the region between exons 1 and 2 (left). Q-RT-PCR analysis of RNAs from HeLa cells treated with siRNAs against PTB, nPTB, UPF1, or combinations. The data presented are means of primer pair expression normalized relative to HPRT expression ± SD of three biological replicates. Light gray bars represent primer pair between exons 1 and b, dark gray represents primer pair between exons b and 2. Asterisk indicates significant differences from control, t test p < 0.05.