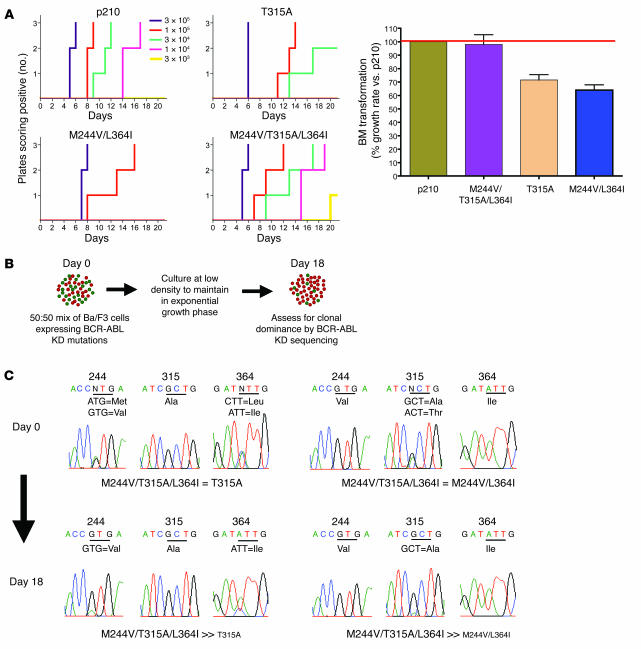
Figure 4. Sequential kinase inhibitor therapy can result in compound mutations that increase transformation potency and growth rate in vitro.
(A) Bone marrow transformation assays with select drug-resistant BCR-ABL kinase domain mutants are shown. After infection with mutant or wild-type p210 BCR-ABL retrovirus, primary mouse bone marrow cells were plated at the serial dilutions indicated then monitored for oncogenic transformation. The time to outgrowth in assays performed in triplicate at 5 separate dilutions is shown on the left, and the right panel shows the percentage growth rate of various BCR-ABL isoforms relative to wild-type BCR-ABL. (B) Schematic of cell growth competition experiment. (C) Representative sequencing results following cell growth competition assay reveal BCR-ABL/M244V/T315A/L364I to be capable of conferring a growth advantage over BCR-ABL/M244V/L364I and BCR-ABL/T315A.