Fig. 4.
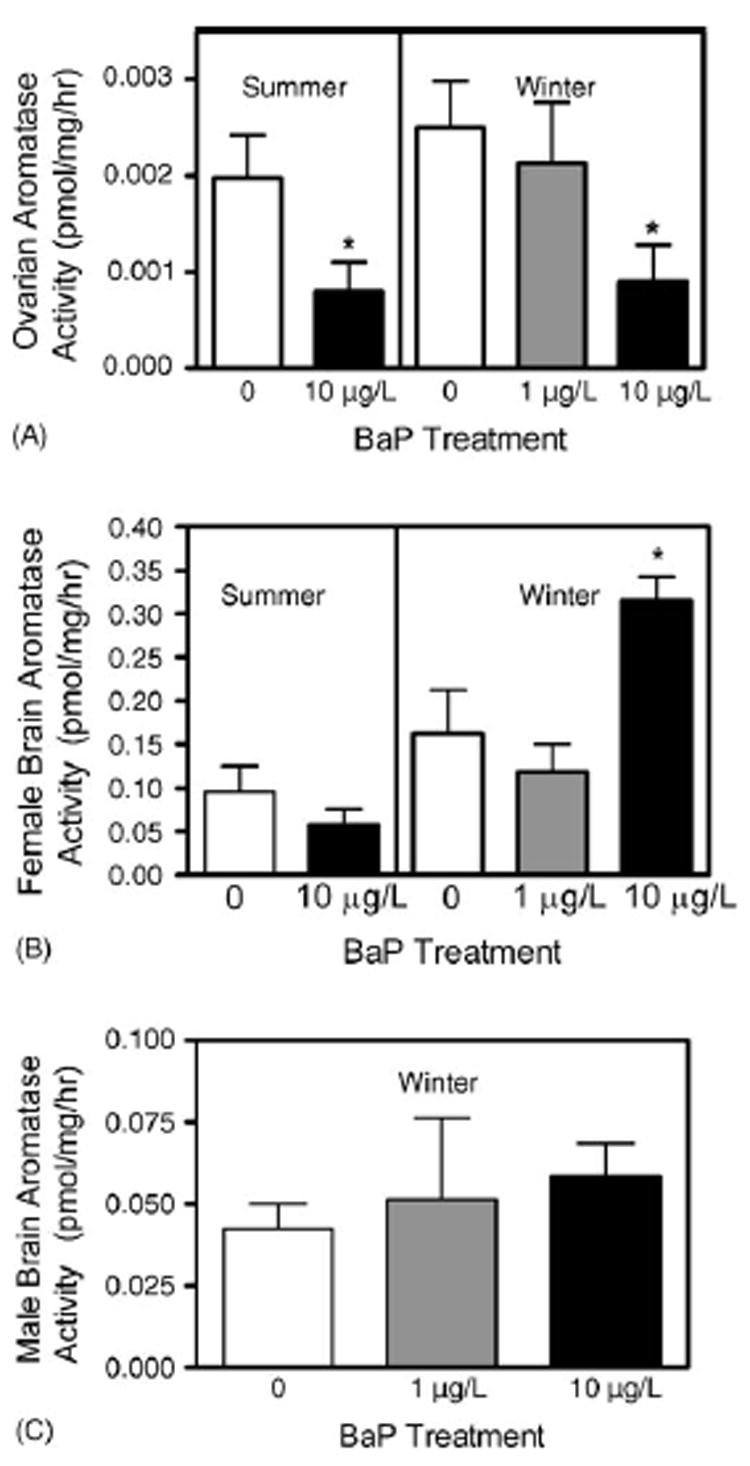
Aromatase activity in killifish exposed to water-borne BaP for 15 days. Ethanol (180 μL) was used as the solvent control. Ovary or brain homogenate (500 or 150 μg protein, respectively) was incubated with 3 nM 3H-androstenedione for 3 h at 28 °C. Aromatase activity was measured as the release of tritiated water and reported as pmol/mg/h. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. of 5–7 fish per treatment. (A) Ovarian activities. Following the summer and winter exposure 10 μg/L BaP inhibited aromatase by 2.5- and 2.8-fold, respectively (p = 0.019, t-test and p = 0.027, ANOVA, respectively). (B) Female brain activities. Summer brain activities were not statistically different from controls (p = 0.275, t-test), however, in winter BaP significantly increased brain activity (p = 0.029, ANOVA). (C) Male brain activities (p = 0.531 ANOVA).
