Fig. 5.
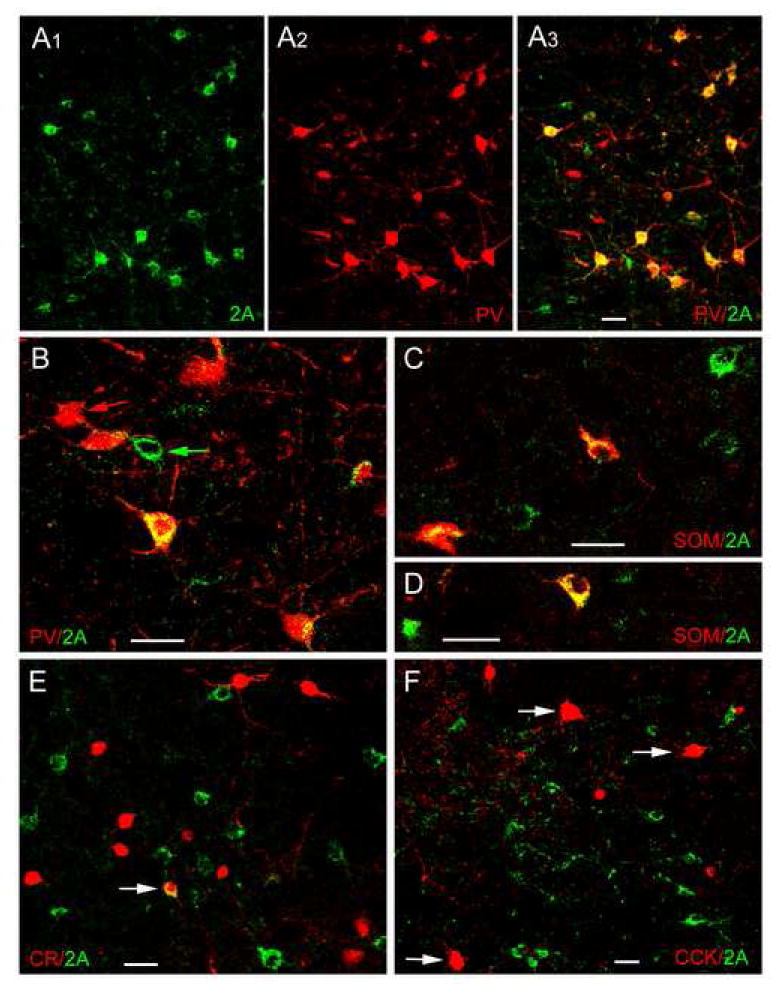
Dual localization of 5-HT2AR immunoreactivity (Oncogene/Calbiochem polyclonal antibody) and interneuronal marker immunoreactivity in the BLa using immunofluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy. A1-A3) Dual localization of 5-HT2AR and PV in the BLa. A1) 5-HT2AR+ neurons (green). A2) PV+ neurons (red) in the same field. A3) Merging of the red and green channels indicates that there is extensive colocalization of 5-HT2AR and PV immunoreactivity (yellow), but there are also neurons that are single-labeled for 5-HT2AR (green) or PV (red). B) Higher power merged image of 5-HT2AR (green) and PV (red) in the BLa. In addition to five PV+ neurons with variable amounts of 5-HT2AR immunoreactivity (yellow), there is also a single-labeled PV+ neuron (red arrow) and a single-labeled 5-HT2AR + neuron (green arrow). C, D) Dual localization of 5-HT2AR (green) and SOM (red) in the BLa. Double-labeled 5-HT2AR/SOM+ neurons (yellow) and single-labeled 5-HT2AR neurons (green) are observed in these two fields. E) Dual localization of 5-HT2AR (green) and CR (red) in the BLa. Arrow indicates one of two double-labeled neurons found in the BLa (see Table 1). F) Dual localization of 5-HT2AR (green) and CCK (red) in the BLa. No colocalization of 5-HT2AR with CCK was observed in either large Type L CCK neurons (arrows) or small Type S CCK neurons (smaller red cells). All scale bars = 25 μm.
