FIG. 3.
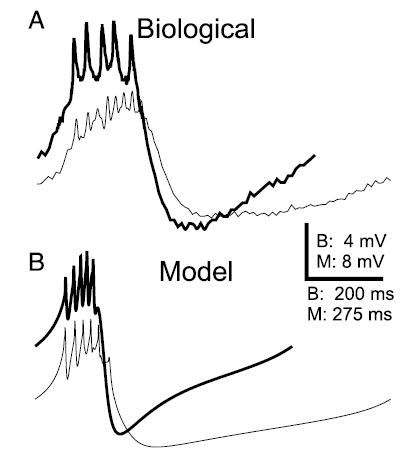
Membrane potential waveform of the AB neuron is changed by electrical coupling to the PD neuron. A: intracellular recordings show the waveforms of an AB neuron when electrically coupled (thin trace) to the PD neuron and when isolated (thick trace). On isolation, the average spike amplitude increased and the average spike number per burst decreased. Minimum Vm (in mV): −61.3 for coupled and −62.9 for isolated AB neuron. B: a comparison of the waveforms in the model AB neuron when it is coupled to the PD neuron (thin trace) and when isolated (thick trace) shows that the isolated AB neuron waveform has a larger amplitude and shorter period, as in the biological neuron. Spike number per burst also decreased. Minimum Vm (in mV): −53.5 for coupled and −58.4 for isolated AB neuron.
