Figure 2.
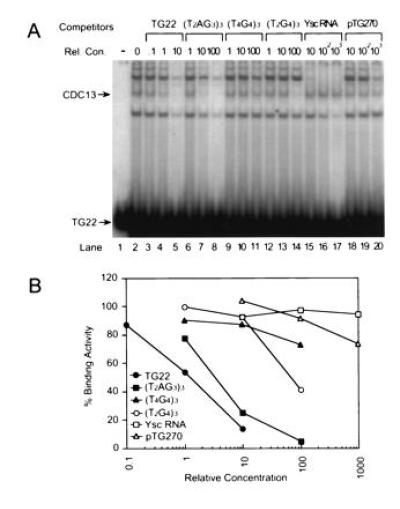
Cdc13p binding is specific. (A) Gel mobility-shift assays were carried out using 1 ng of 32P-labeled TG22 and 10 μg of E. coli extract from cells expressing Cdc13p. Prior to loading the gel, the TG22 was mixed with unlabeled ss oligonucleotides of the sequence and at the relative concentration (Rel. Con.) indicated above each lane or with total yeast RNA or pTG270, a 6300-bp plasmid containing 270 bp of C1–3A/TG1–3 DNA. The Cdc13p–TG22 complex is indicated by the arrow. Lane 1 had no extract. (B) The amount of gel shift activity in the Cdc13p-TG22 complex was quantified for each oligonucleotide at each concentration. Relative concentration of competitor nucleic acids in all gels was expressed as the ratios of the amount of ss TG1–3 DNA in the competitor to the amount of ss TG1–3 DNA in TG22 (see Materials and Methods); for competitors that did not have ss TG1–3 DNA (e.g., Ysc RNA), it was expressed as the ratio of nanograms of competitor to nanograms of TG22. In this and subsequent gels, the amount of gel shifted complex in TG22 with no competitor was defined as 100%. The values presented are the average of two independent experiments; for each point, the two values were within 14% of each other.
