Figure 1.
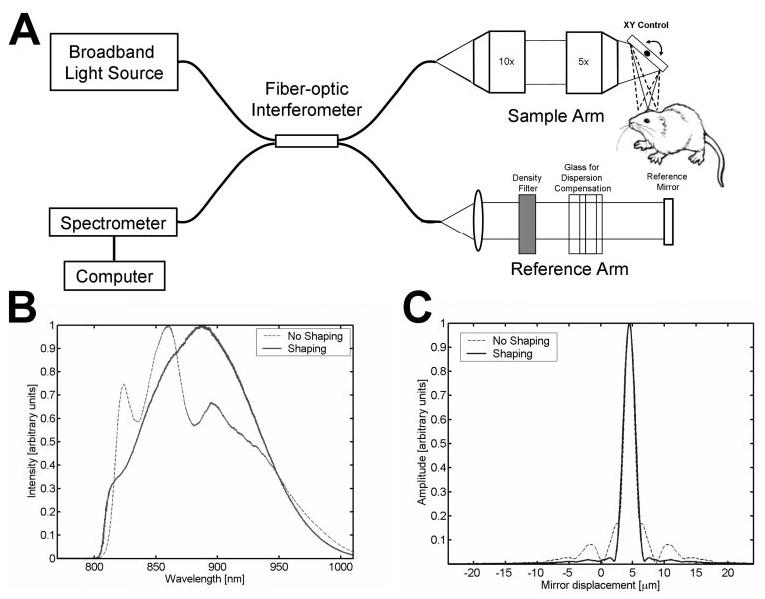
(A) Schematic of high-speed, ultrahigh-resolution OCT system for rat and mouse retinal imaging. Imaging is performed using contact lens and postobjective scanning. Spectral and Fourier domain detection are performed with a high-speed, high-resolution spectrometer. (B) Spectrum of the light source detected by the spectrometer, with and without numerical spectral shaping to smooth the spectrum. The compact, multiplexed superluminescent diode light source has BW = 145 nm at λc = 890 nm. (C) Axial PSF and without spectral shaping to reduce side lobes. The axial resolution is 2.8 μm in tissue.
