Fig. 3.
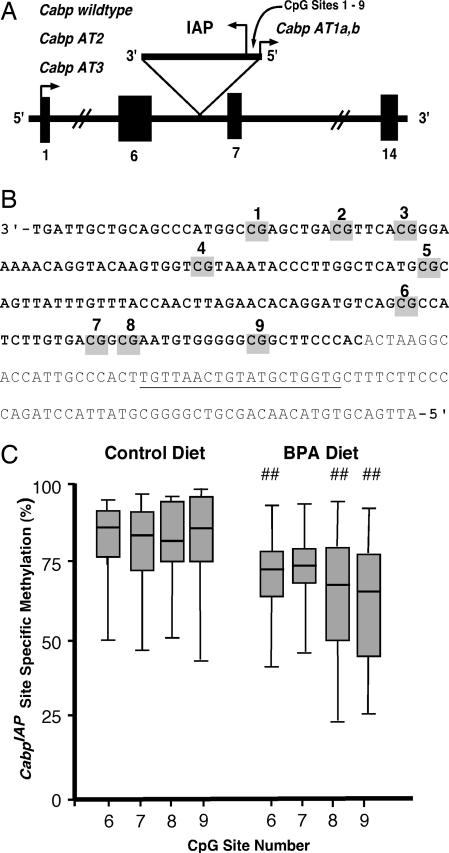
Maternal BPA exposure decreases offspring methylation at the CabpIAP metastable epiallele. (A) The CabpIAP metastable epiallele (17) contains a contra-oriented IAP insertion within intron 6 of the murine CDK5 activator-binding protein (Cabp) gene, resulting in short aberrant transcripts originating from the 5′ LTR of the IAP (short arrowhead labeled “Cabp AT1a,b”). Short aberrant transcripts also originate at the normal transcription start site (short arrowhead labeled “Cabp wild type”) because of premature truncation upstream of the IAP insert (Cabp AT2 and AT3). Normal Cabp transcription covers 14 exons, resulting in a 2-kb transcript. (B) The IAP sequence containing nine CpG sites located between the cryptic Cabp promoter and the IAP promoter (bold text) and the downstream 3′ genomic sequence (nonbold text). The location of the bisulfite-converted genomic reverse primer for amplifying the 5′ CabpIAP locus is underlined. (C) Box plots representing the percentage of cells methylated at CpG sites 6–9 in control (n = 39) and BPA-exposed (n = 39) Avy/a offspring (diet group t test; ##, P < 0.01).