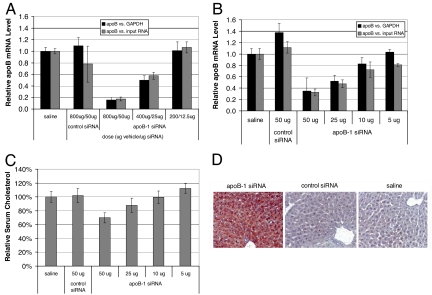
Fig. 5.
apoB-1 siRNA polyconjugate dose–response and phenotypes of treated mice. (A) Knockdown of apoB mRNA after injection of serial dilutions of the apoB-1 siRNA polyconjugate. The indicated dose of apoB-1 or control siRNA polyconjugate was injected intravenously in mice. The livers were harvested 2 days later, and the relative levels of apoB mRNA to those of GAPDH mRNA or total input RNA were measured by RT-qPCR. Data are normalized to mice receiving saline alone. n = 5, data are shown as mean ± SD. (B) Reducing the amount of apoB-1 siRNA attached to the polyconjugate decreases apoB knockdown. Mice were injected with polyconjugate (800 μg of polymer) covalently attached to the indicated amount of apoB-1 or control siRNA. The livers were harvested and relative apoB mRNA levels were determined as in A. n = 5, data are shown as mean ± SD. (C) Serum cholesterol is reduced in a siRNA dose-dependent manner in mice treated with apoB-1 siRNA polyconjugate. Serum from mice in B was collected after a brief fast (4 h) and analyzed for total cholesterol. Values were normalized to mice receiving saline only. n = 5, data are shown as mean ± SD. (D) Knockdown of apoB results in increased hepatic lipid content. Liver sections were taken from briefly fasted mice 2 days after injection of apoB-1 or control siRNA polyconjugate (800 μg of polymer, 50 μg of siRNA), or saline only. Sections were fixed, and lipids were detected by staining with oil red.