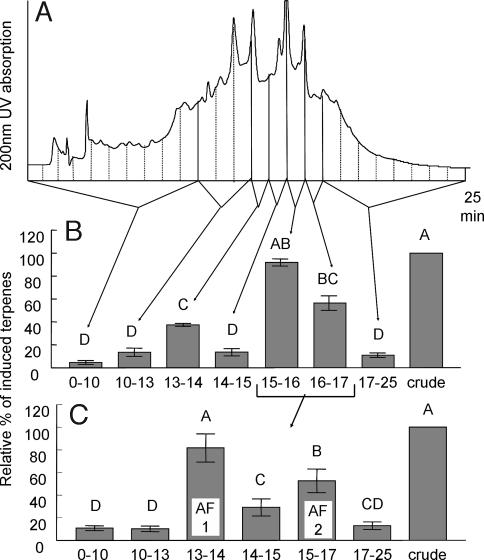
Fig. 1.
HPLC separation and bioassay results of collected fractions. (A) Chromatographic trace (using 200-nm UV detection and pH 4.5 solvent) and 1-ml fraction collection of protein-precipitated and solid-phase extraction (SPE)-purified S. Americana regurgitant. (B) Bioassay results (n = 20) of combined fractions showing strong activity in the 15- to 17-min region and some activity in the 13- to 14-min fraction. (C) Bioassay result (n = 12) of the combined fractions 15–17 min from B after repeated HPLC. Separation was achieved using a neutral (pH 7) solvent and a slow gradient. The active 13- to 14-min fraction was assigned active fraction 1 (AF1) and the 15- to 16-min fraction was assigned AF2. The excised plant assay was used for all bioassays, and the induced volatile release was normalized and analyzed statistically (P < 0.01) as described in Methods.