Fig. 2.
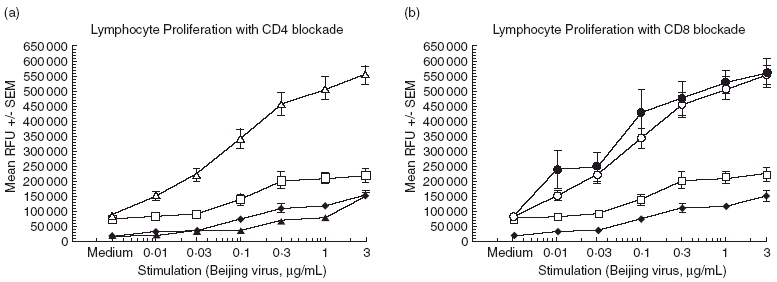
Proliferation in response to antigen is CD4 T cell-dependent. BALB/c mice (six per group) were immunized with 10 µg Beijing influenza virus and 100 µg T cell immunoglobulin mucin-1 (TIM-1) antibody or isotype control. After 21 days, the splenocytes were harvested and cultured as described. Antigen-stimulated proliferation of lymphocytes in the presence of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 antibodies was compared to lymphocytes stimulated in the absence of blocking antibodies. Antibodies specific for CD4 or CD8 were added to wells containing lymphocytes to a final concentration of 10 µg/ml and allowed to incubate for 96 h in culture prior to analysis. (a) Open triangles, stimulation in the absence of anti-CD4; black triangles, with anti-CD4. (b) Open circles, stimulation in the absence of anti-CD8; black circles, with anti-CD8. Control groups for both (a) and (b): open squares, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) vaccination; black diamonds, Beijing virus vaccination only. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisk for values compared to stimulation in the presence of blocking antibodies. ***P < 0·001.
