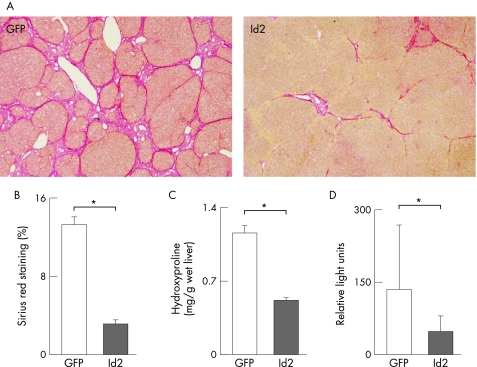
Figure 6 Preventive effect of Id2 expression on the progression of TAA‐induced hepatic fibrosis. Rats were treated with 200 mg/kg body weight of TAA twice a week for 4 weeks and then injected with 2.0×109 PFU of CAG‐Cre and LNL‐Id2 via the tail vein. TAA injection was continued for the next 3 weeks and the animals were then sacrificed. (A) Sirius red staining. Note that fibrotic septa caused by TAA treatment (control) were dramatically suppressed by Id2 expression induced by CAG‐Cre and LNL‐Id2 injection. Rats co‐infected with LNL‐GFP were used as controls. (B, C) Estimation of liver fibrosis. The degree of hepatic fibrosis was quantified by measuring the area positive for Sirius red staining (B) and hydroxyproline content (C). Data obtained from eight rats in each group are given as means±SD. *p<0.05. (D) COL1A2 mRNA was analysed using real‐time RT‐PCR as described in the Methods section. Relative expression of COL1A2 mRNA was normalised against that of GAPDH mRNA. Data obtained from six rats in each group are given as means±SD. *p<0.05.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.