Figure 1.
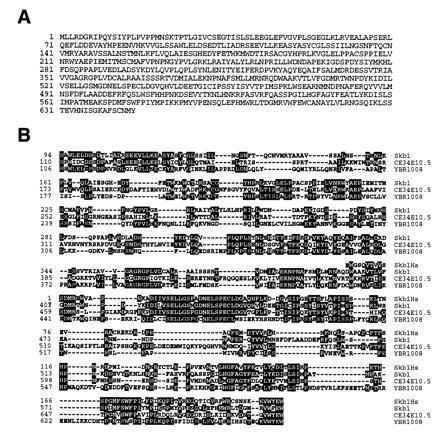
Deduced amino acid sequence of Skb1 and alignment of Skb1-related proteins encoded by open reading frames in the genomes of C. elegans and S. cerevisiae and by an uncharacterized human cDNA sequence. (A) Deduced amino acid sequence of the skb1 gene product. (B) blast searches of nucleic acid data bases revealed the existence of a human cDNA sequence, which we have named HsSkb1, and open reading frames in C. elegans (CE34E10.5) and S. cerevisiae (YBR1008) encoding predicted polypeptides with significant structural homology to Skb1. Alignments were generated using the LaserGene megalign program (DNAStar). Identical amino acid residues are indicated by black boxes. The HsSkb1 sequence was derived from four overlapping human expressed-sequence tag cDNA clones (GenBank accession nos. F12149F12149, H25612H25612, R65681R65681, and T69495T69495). The polypeptide encoded by the entire partial length HsSkb1 cDNA is shown. Residues 110–690 of the 1281 amino acid protein predicted by the CE34E10.5 ORF are shown, while residues 106-677 of the 827 amino acid protein predicted by YBR1008 are shown. Skb1 and HsSkb1 exhibit 47% identity over a span of 213 amino acids. Over its entire length of 646 amino acids, Skb1 is 35% identical to C34E10.5 and 33% identical to YBR1008.
