Fig. 7.
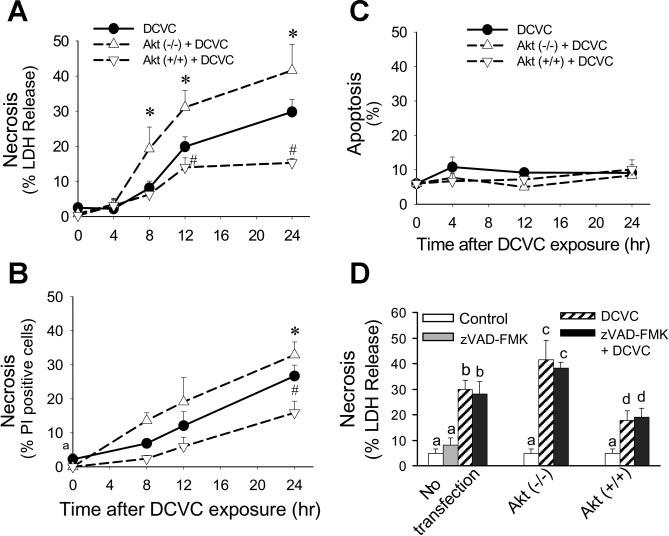
Effect of modulation of Akt activation on RPTC necrosis (A: measured using LDH release as marker, B: measured by flow cytometric analysis of propidium iodide-positive and annexin V-FITC-negative cells) and apoptosis (C) at different time points following DCVC (240 μM) exposure. D: effect of caspase inhibition (50 μM, zVAD-FMK) on DCVC-induced necrosis in RPTC at 24 h following DCVC exposure. Akt (−/−) RPTC infected with adenovirus carrying dominant negative (inactive) Akt (MOI = 21). Akt (+/+) RPTC infected with adenovirus carrying constitutively Akt (MOI = 27). The results are means ± SE (n = 5). Values with dissimilar superscripts (a, b, c, d) are significantly (P < 0.05) different from each other.
