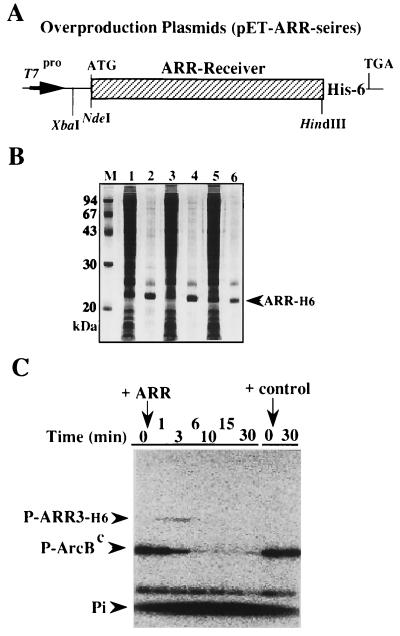
Figure 3.
Isolation of the ARR receiver domains and characterization of their in vitro activity. (A) Plasmids (pET-ARR series) were used to overexpress the ARR receiver domains in E. coli. The ARR genes can be expressed from plasmids under the T7 phage promoter, and the presumed ARR translation products were followed by a histidine tag (His × 6) at their C termini. (B) These overexpressed ARR products (designated as ARR-H6) were analyzed by SDS/PAGE (lane 1, ARR3-H6; lane 3, ARR4-H6; lane 5, ARR6-H6). They were then purified by Ni-column chromatography (lane 2, ARR3-H6, lane 2, ARR4-H6; lane 6, ARR6-H6). These samples were used for the following experiment. (C) In vitro analyses of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the ARR receiver domains. The purified ArcBc polypeptide (HPt domain) was 32P labeled (lane 0, designated as P-ArcBc), as described (7, 9). This preparation was incubated with ARR3-H6. At intervals (indicated by min), samples were immediately analyzed by SDS/PAGE, followed by autoradiography. Note that ARR3-H6 was rapidly phosphorylated and dephosphorylated. Appropriate control experiments are described in the text.