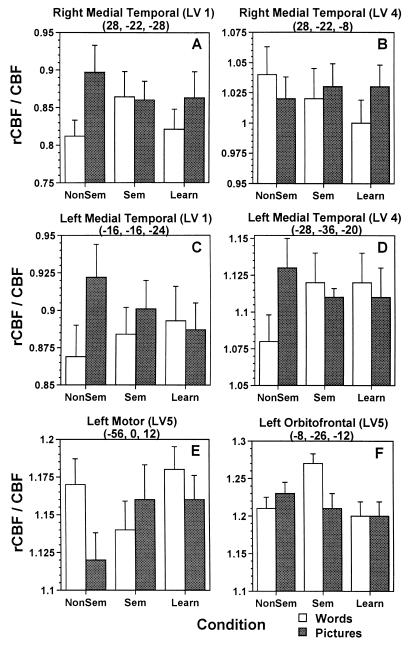
Figure 2.
Ratios of rCBF to whole brain CBF in areas of the brain that showed interactions between stimulus type and encoding condition. The medial temporal regions from LV1 (A and C, coordinates shown in parentheses) showed greater rCBF during picture encoding compared with word encoding (P < 0.001 for the right hemisphere and P < 0.02 for the left). These regions also had condition × stimulus interactions by univariate test (both P < 0.05), indicating a larger difference between pictures and words in the nonsemantic condition. B and D show medial temporal regions from LV4 that showed stimulus × encoding interactions involving the nonsemantic and intentional learning conditions (univariate interaction for right hemisphere P = 0.02; left hemisphere P = 0.07). E and F show regions from LV5 with stimulus × encoding interactions involving nonsemantic and semantic conditions (univariate interaction for left motor region, P = 0.01; interaction for left orbitofrontal region, P = 0.006). Additional regions with stimulus × encoding interactions are shown in Table 3. nonsem, nonsemantic encoding; sem, semantic encoding; learn, intentional learning.