Figure 3.
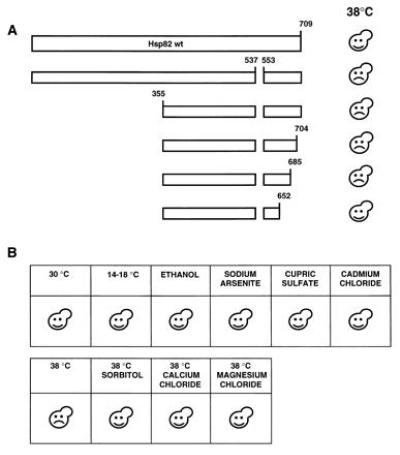
Characterization of a dominant negative Hsp82 mutant. (A) Schematic representation of a deletion analysis of the dominant negative mutant Hsp82-(Δ538-552). Plasmids encoding Hsp82 mutants were introduced into a wild-type yeast strain and transformants were streaked onto minimal plates and incubated at 30°C or 38°C. (B) The dominant negative effect is limited to heat stress. A wild-type yeast strain expressing the dominant negative Hsp82 mutant was streaked onto minimal plates. Where indicated, 6% ethanol, 0.1 mM sodium arsenite, 3 mM cupric sulfate, 10 μM cadmium chloride, 1 M sorbitol, 100 mM calcium chloride, and 100 mM magnesium chloride were added. Unless indicated, plates were incubated at 30°C. Happy and sad faces indicate that the transformants succeeded or failed, respectively, to grow.
