Fig. 1.
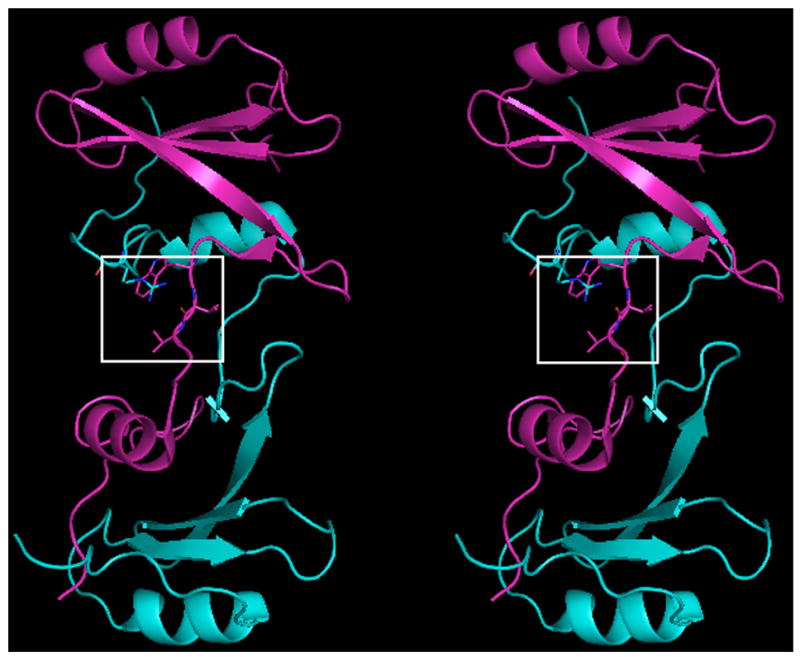
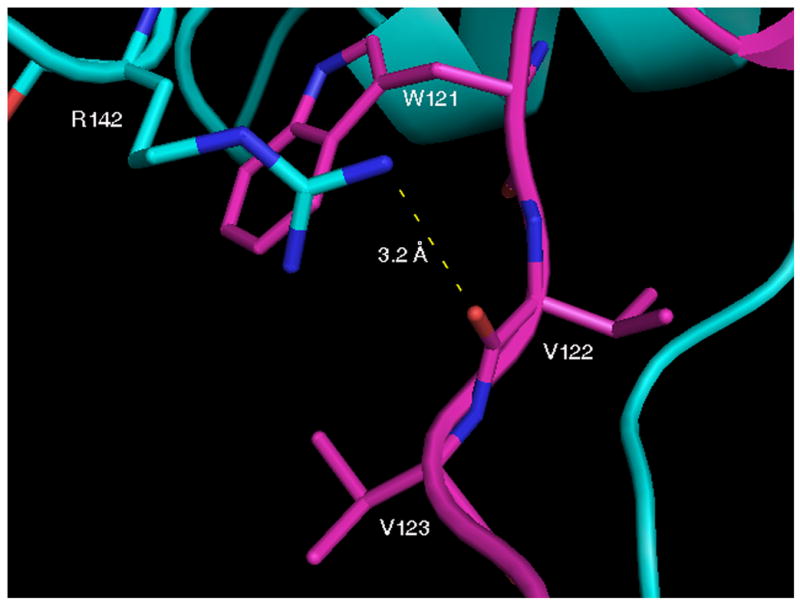
Crystal structure of native domain-swapped dimeric Grb2-SH2. A, Cross-eyed stereo view of native domain-swapped dimeric Grb2-SH2, generated by applying crystallographic symmetry. The two molecules composing the dimer, shown in magenta and cyan, swap the C-terminus, composed of residues 124–152. B, In domain-swapped dimeric Grb2-SH2 residues 121–123 are in an extended conformation, which allows for a hydrogen bond (dashed yellow line) to form between the □guanidine group of R142 and the carbonyl oxygen atom of V122. The side chains of R142 and V123 mostly bury W121.
