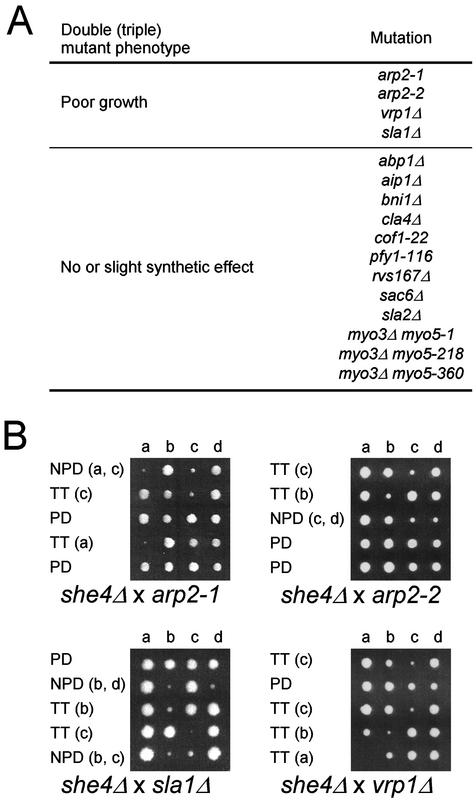
Figure 4.
Genetic interactions between SHE4 and actin-related genes and MYO5. (A) Summary of genetic interactions. Each mutant strain was crossed with she4Δ (YKT275 or YKT276), and resultant diploid cells were sporulated and dissected for tetrad analysis. The growth characteristics of the resulting double or triple mutants were determined at 25°C. The mutant strains used were YMW211U (arp2-1), YMW221U (arp2-2), YKT130 (vrp1Δ), YKT218 (sla1Δ), DDY322 (abp1Δ), DDY1520 (aip1Δ), YKT382 (bni1Δ), YKT388 (cla4Δ), DDY1226 (cof1-22), DDY1024 (pfy1-116), DDY949 (rvs167Δ), DDY318 (sac6Δ), YKT186 (sla2Δ), YKT91 (myo3Δ myo5-1), YKT93 (myo3Δ myo5-218), and YKT111 (myo3Δ myo5-360). (B) Genetic interactions of arp2-1, arp2-2, sla1Δ, and vrp1Δ with she4Δ mutation. Diploid cells obtained from an indicated cross were sporulated, dissected, and grown at 25°C for 3–4 d before being photographed. Colonies were then replica plated to determine the segregation of the marked mutant alleles. Tetrad genotype (TT, tetratype; PD, parental ditype; and NPD; nonparental ditype) is indicated, and the identity of the double mutant spore(s) is shown in parentheses.