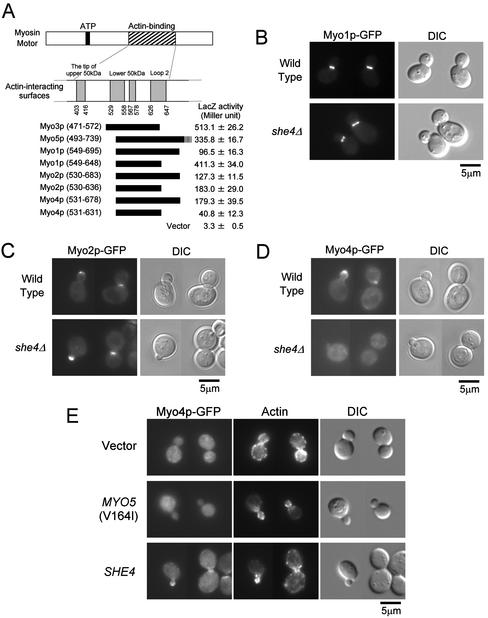
Figure 8.
She4p interacts with type II and type V myosins and is required for proper localization of Myo4p. (A) Two-hybrid interactions between She4p and myosins. DNA fragments encoding Myo1p, Myo2p, and Myo4p were cloned into pGAD vectors. The resultant plasmids were introduced into L40 cells carrying pKT1295. The interaction between the UCS domain of She4p and myosins were examined quantitatively by β-galactosidase activity assay. The myosin motor regions used in the experiment were represented schematically. The numbers below actin-binding surfaces and in parentheses represent amino acid positions in chicken skeletal muscle myosin and each yeast myosin, respectively. β-Galactosidase (LacZ) activity represents the average and SD for three independent transformants. (B) Localization of Myo1p-GFP in she4Δ cells. Myo1p-GFP–expressing cells of YKT640 (wild-type) and YKT641 (she4Δ) were exponentially grown at 25°C. Myo1p-GFP was visualized using a GFP band pass filter (Myo1p-GFP). The same exposure and processing parameters were used for comparison. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Localization of Myo2p-GFP in she4Δ cells. YKT520 (wild-type) and YKT524 (she4Δ) were observed as described in B. Bar, 5 μm. (D) Localization of Myo4p-GFP in she4Δ cells. YKT544 (wild-type) and YKT543 (she4Δ) were observed as described in B. Bar, 5 μm. (E) Delocalization of Myo4p-GFP in she4Δ mutant is not due to depolarization of the actin cytoskeleton. Myo4p-GFP–expressing cells, YKT543, were transformed with YEplac195 (vector), pKT1332 [MYO5 (V164I)], or pKT1290 (SHE4). Transformants were exponentially grown in SDA-Ura at 25°C, fixed, and stained with TRITC-phalloidin. Localization of Myo4p-GFP and F-actin was visualized with a GFP band pass filter (Myo4p-GFP) and a TRITC filter (actin), respectively. For each observation, the same exposure and processing parameters were used. Bar, 5 μm.