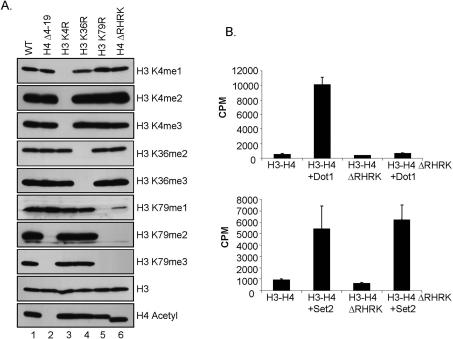
Figure 2.
A basic patch of amino acids in histone H4 is required for H3K79 methylation in vivo. (A) Western blots of whole-cell extracts using methyl-specific antibodies show the methylation status of H3K4, H3K36, and H3K79 in yeast cells expressing wild-type histones or cells expressing the indicated histone mutants. Antibodies directed against histone H3 and acetylated H4 serve as loading controls. Cells expressing mutant histones H3K4R, H3K36R, or H3K79R serve as negative controls for the indicated histone antibodies. (B) Dot1 is not active on yeast chromatin substrates isolated from cells lacking the basic patch of histone H4 in vitro. Recombinant-purified Dot1 (1.2 μg) was incubated with soluble chromatin substrates isolated from yeast cells expressing either wild-type histone H4, or from cells expressing histone H4 lacking the basic amino acids R17–K20 (H4ΔRHRK) in the presence of 3H-SAM in an in vitro HMTase assay. Incorporation of 3H-Methyl was measured by scintillation. Recombinant-purified Set2 (2.0 μg) was used as a control.