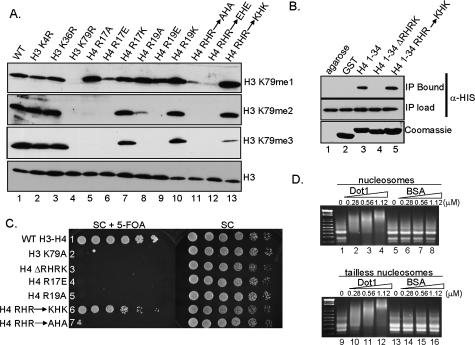
Figure 3.
Basic amino acid residues within the basic patch of histone H4 are necessary for H3K79 methylation, Dot1 H4–tail interactions, and telomere silencing. (A) Western blots were performed using whole-cell extracts from cells expressing wild-type histones or the indicated histone mutations. The methylation status of H3K79 was examined using methyl-specific antibodies directed against H3K79me1, H3K79me2, and H3K79me3. Antibodies specific for histone H3 were used as a loading control. (B) In vitro binding assays were performed to test if Dot1 interacts with the H4 N-terminal tail. Bacterial cell extracts from cells expressing recombinant His6-Dot1 were incubated in the presence of a GST-H4 tail encoding residues 1–34 of histone H4 (GST-H41–34; lane 3), GST-H41–34 lacking the basic amino acids R17–K20 (GST-H41–34ΔRHRK; lane 4), and GST-H41–34 containing R17K and R19K mutations (GST-H41–34RHR–KHK; lane 5) bound to glutathione agarose beads. Bound His6-Dot1 was detected by α-HIS antibodies. (Top panel, lane 2) GST-bound beads or glutathione agarose beads alone were incubated with Dot1 extracts as negative controls. (Middle panel) Reaction inputs were probed with α-HIS antibodies to confirm equivalent amounts of Dot1 (IP load). GST-histone constructs were Coomassie-stained to indicate the amount of GST histone fusion protein loaded per lane. (C) Maintenance of charge of the H4 basic patch is required for telomere silencing. Strain UCC1369 (URA3-TEL-VIIL), expressing the indicated histone mutations, was grown to saturation, normalized to OD600, serially diluted (4×), and spotted on SC or SC + 5-FOA media. UCC1369 expressing wild-type histones and H3K79A served as controls for telomere silencing assays; cells were grown on SC media as a growth control. (D) Nucleosome-binding gel mobility assays were performed using chicken erythrocyte nucleosomes and recombinant-purified His6-Dot1. Wild-type nucleosomes (lanes 1–8) and tailless nucleosomes (lanes 9–16) were used as substrates. BSA was used as a control. The concentration of purified proteins in each reaction is indicated.