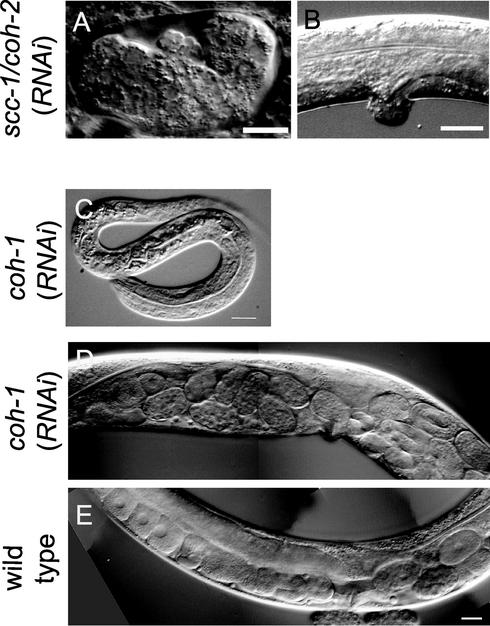
Figure 2.
SCC-1/COH-2 and COH-1 play distinct roles in development. (A and B) SCC-1/COH-2 is required for mitotic division throughout development. Depletion of SCC-1/COH-2 in embryos resulted in embryonic lethality. A terminally arrested embryo is shown in A. When the function of SCC-1/COH-2 was depleted postembryonically, some worms exhibited abnormal morphology of the vulva (B). (C–E) COH-1 is essential for larval development and the egg-laying ability. Some coh-1(RNAi) F1 progeny arrested as L1 larvae (C). When the function of COH-1 was disrupted in L1 worms by RNAi by soaking, coh-1(RNAi) adults showed an egg-laying defect, accumulating more eggs in the gonad (D) than wild-type hermaphrodites (E). Bar, 10 μm (A and C), 20 μm (B), and 20 μm (D and E).