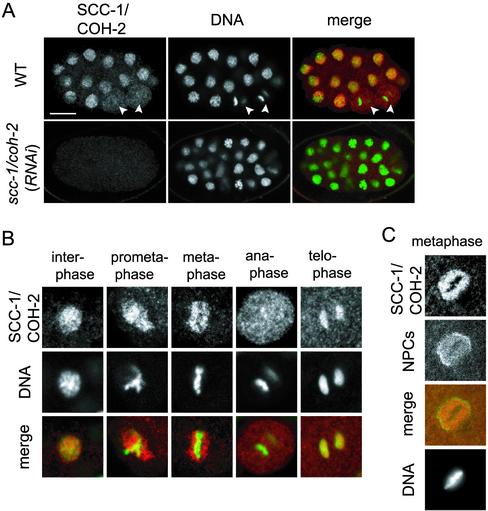
Figure 3.
Cell cycle-dependent localization of SCC-1/COH-2 in early embryos. (A) Wild-type and scc-1/coh-2(RNAi) embryos were stained with anti-SCC-1/COH-2 antibodies (SCC-1/COH-2, red) and Sytox Green (DNA, green). The white arrowheads indicate anaphase cells, in which SCC-1/COH-2 is dissociated from the chromosomes and dispersed in the whole cytoplasm. The SCC-1/COH-2 signal was not detected in scc-1/coh-2(RNAi) embryos. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Magnified images of nuclei in wild-type early embryos. SCC-1/COH-2 accumulated in the interphase nuclei but was not detectable on condensed metaphase chromosomes. SCC-1/COH-2 associated again with chromosomes at telophase. (C) Wild-type nuclei in an early embryo were stained with anti-SCC-1/COH-2 antibodies (SCC-1/COH-2, red), an anti-nuclear pore complexes antibody (NPCs, green), and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DNA). It is noticeable that few SCC-1/COH-2 molecules associate chromosomes at metaphase but they stay in the nucleoplasm surrounded by the nuclear membrane.