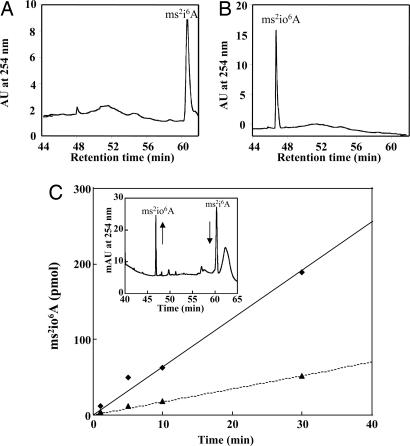
Fig. 1.
HPLC chromatograms of tRNA hydrolysates. (A) tRNAs were obtained from E. coli DH5α strain. (B) tRNAs were obtained from an in vivo complementation of DH5α strain transformed with pT7-miaE2 or pT7-miaE2H. The identification of ms2i6A and ms2io6A was based on UV-visible spectra (data not shown) and retention times (ms2i6A eluted at ≈60 min and ms2io6A at ≈47 min). (C) ms2io6A production as a function of reaction time and quantity of purified MiaE2H enzyme (♦, 20 μM; ▴, 5 μM). The assay mixture contained 50–100 μg of bulk tRNAs and 0.6 mg of cell-free extracts in 100 mM Tris·HCl (pH 7.5). Reactions were carried out at 37°C. (Inset) The HPLC detection of ms2i6A substrate (elution at 60 min) and ms2io6A, product of the reaction (elution at 47 min) the arrows indicate the decrease of the substrate and the increase of the product.