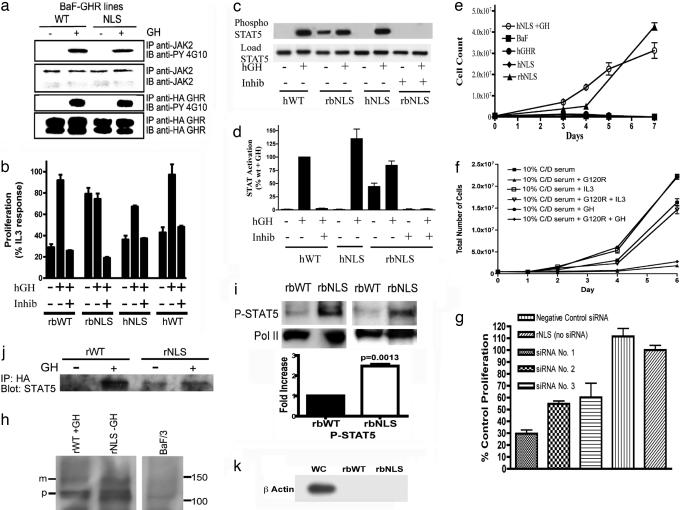
Fig. 6.
Mechanistic studies. (a) Activation of WT and NLS GHR in BaF lines as determined by tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK2 and GHR in phosphotyrosine immunoblots. BaF-GHR WT or NLS lines were serum-starved for 6 h and then treated with human GH (100 ng/ml) (+) or saline (−) for 10 min. (b) Proliferative response of BaF lines, and abrogation of this with JAK2 inhibitor 1 (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) at 0.4 μM, using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay (MTT) (SI Text). (c) STAT5 activation in BaF lines showing constitutive activation in BaF-NLS and abrogation by JAK inhibitor, with quantification for three independent experiments (d). (e) Proliferation of BaF lines from 0.5 × 106 cells showing lack of constitutive proliferation with NLS-human GHR cells. (f) G120R (0.6 μM) blocks constitutive proliferation of NLS-rbGHR expressing cells growing in charcoal stripped serum (g) siRNA to murine GH inhibits constitutive proliferation in charcoal stripped serum (h) mature and precursor full-length GHR in highly purified BaF cell nuclei prepared according to (28). (i) Enhanced basal (2.5-fold by densitometry) phospho-STAT5 (Cell Signaling clone 14H2, Y694) in purified nuclei of NLS-rbGHR BaFcells. Histogram shows quantification of three separate preparations, mean ± SEM (j) STAT5 coimmunoprecipitation with nuclear GHR, even in the basal state with NLS-GHR BaF cells. (k) β-Actin immunoblot comparing whole-cell and nuclear β-actin with 10 μg of protein, demonstrating purity of nuclei in i.