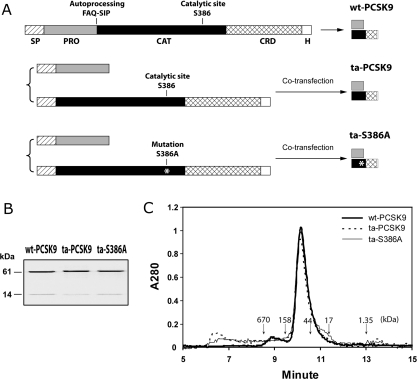
Figure 1. Production of the ta-S386A mutant.
(A) Schematic diagram of the expression strategy for wt-PCSK9, ta-PCSK9 and ta-S386A proteins. The wt-PCSK9 protein is expressed from a single construct as described in the Methods section. The single-chain precursor is biosynthesized in the ER, auto-cleaved between Gln152 and Ser153, and secreted as a prodomain–catalytic domain bound complex. The ta-PCSK9 and ta-S386A proteins are produced with a two-plasmid co-transfection strategy, as described in the Methods section. The prodomain and catalytic domain of PCSK9, either wt or bearing the S386A mutation, are translated in the ER via separate secretion signal peptides, then folded in trans, assembled and secreted in the same complex form as wt-PCSK9. Segments on each construct are indicated as follows: SP, signal peptide; PRO, prodomain; CAT, catalytic domain; CRD, cysteine-rich domain; H, hexahistidine tag. (B) Electrophoretic analysis of purified PCSK9 variants. All PCSK9 variants were affinity purified via the C-terminal hexahistidine tag and were subjected to reducing SDS/PAGE (0.5 μg of protein per lane). The prodomains (14 kDa) and mature PCSK9 subunits (61 kDa) were visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. (C) Analytic size-exclusion chromatography of PCSK9 variants wt-PCSK9, ta-PCSK9 and ta-S386A. Purified samples (30 μg) were subjected to gel filtration on a Shodex KW-803 column equilibrated with 20 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.6), 200 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP [tris-(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine]. Molecular mass references are indicated by downward arrows: thyroglobulin (670 kDa), γ-globulin (158 kDa), ovalbumin (44 kDa), myoglobin (17 kDa) and vitamin B12 (1.35 kDa).