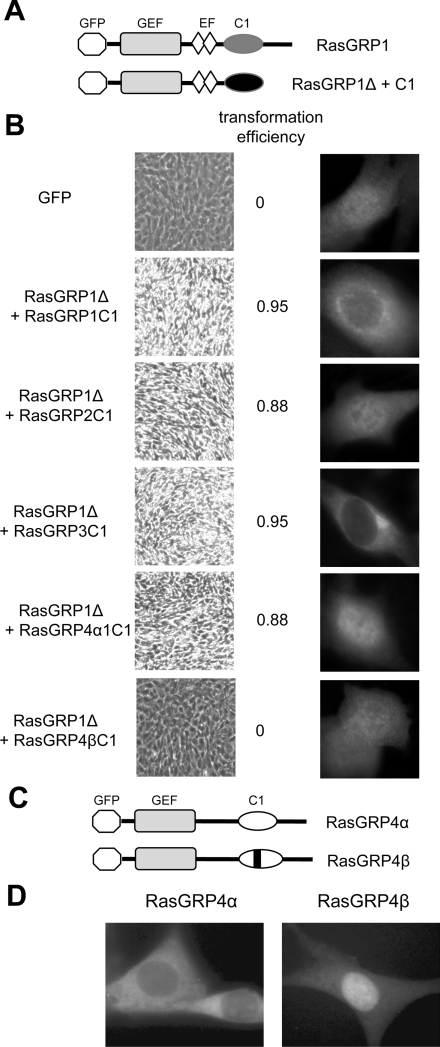
Figure 9. The C1 domains of RasGRP1, RasGRP2, RasGRP3 and RasGRP4α are functional within RasGRPs, whereas the C1 domain of RasGRP4β is not.
(A) Structure of RasGRP1 compared with the deleted form of RasGRP1 used to test functionality of attached C1 domains. The GEF (guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor) domains, EF (EF hand domains) and C1 domains are shown, along with the N-terminal GFP tag. (B) NIH 3T3 cells expressing the indicated RasGRP1Δ+C1 fusion proteins or expressing GFP alone as a control, were assessed for oncogenic transformation (low-magnification pictures of cell cultures, left-hand panel, with high refractility and loss of contact inhibition indicating transformation), and for localization of the GFP-tagged proteins (higher-magnification fluorescence microscopy of typical individual cells, right-hand panel). The efficiency of transformation of each construct was determined as described in the Materials and methods section. (C) Structures of GFP-tagged RasGRP4α and β. The bar represents the five-amino-acid insertion in the C1 domain. (D) NIH 3T3 cells were transduced with retroviral vectors expressing the GFP-tagged RasGRP4 constructs and imaged by fluorescence microscopy.