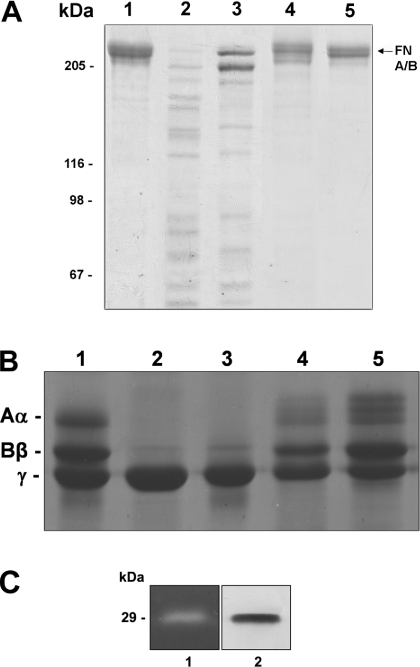
Figure 7. Proteolytic effect of LALP on fibronectin, fibrinogen and gelatin.
Purified fibronectin (A) and fibrinogen (B) were incubated with LALP at 37 °C for 16 h, with a substrate/toxin ratio of 25:1. For the negative control, protein substrates were incubated under similar conditions with a recombinant toxin devoid of proteolytic activity, but obtained under the same conditions for LALP. Samples were subjected to SDS/PAGE (7.5% gel for fibronectin; 10% gel for fibrinogen) under reducing conditions, and gels were stained with Coomassie Blue. Lane 1, purified substrates without toxin treatment; lane 2, substrates incubated with whole venom; lane 3, substrates exposed to LALP; lane 4, substrates incubated with LALP in the presence of 1,10-phenanthroline (5 mM); lane 5, substrates incubated with a recombinant toxin without proteolytic activity. Positions of fibrinogen A(α), B(β) and γ chains and fibronectin A and B chains that co-migrate (FN A/B, arrow) are indicated. Molecular-mass markers are shown on the left. Additionally, the enzymatic function of the recombinant toxin was assessed through a zymogram copolymerized with gelatin (C). Lane 1 demonstrates the gelatinolytic activity of LALP, and lane 2 depicts an immunoblot using antibodies against LALP.