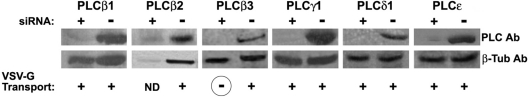
Figure 5. Expression of different PI-PLCs' siRNAs, and their effect on VSV-G transport.
HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs in order to block specific PI-PLCs. The resulting extracts prepared 72 h post-transfection were analysed by Western blot for each corresponding PLC (left upper lane for each protein), and then compared with non-transfected cellular extracts (right upper lane). As a control for protein expression, the extracts were monitored for β-tubulin expression (lower lanes). In a parallel experiment, siRNA-treated cells were transfected with GFP–VSV-G tsO45 48 h after siRNA transfection. After 24 h of VSV-G expression, cells were temperature-shifted as described in the Experimental section, and analysed by immunofluorescence to monitor the localization of VSV-G in the cell. Blocking of TGN to plasma membrane transport (circled ‘–’) was considered when less than 20% of GFP–VSV-G reached the cell surface, and normal transport (+) when more than 75% of the VSV-G-expressing cells had this protein localized at the plasma membrane. No data (ND) were collected from PLCβ2-siRNA-transfected cells, since they died 24–36 h post-siRNA transfection. Corresponding molecular masses in kDa are: PLCβ1: 134; PLCβ2: 130; PLCβ3: 132; PLCγ1: 142; PLCδ1: 83; and PLCϵ: 250. All siRNA Western blots and transport experiments were repeated four times.