Figure 2.
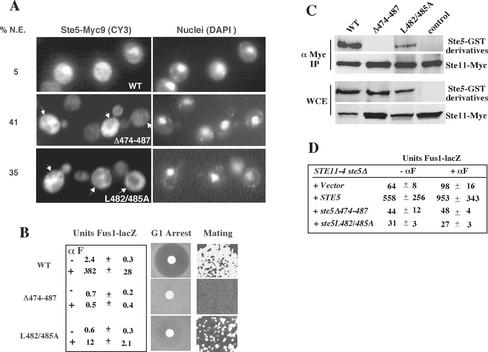
Mutations in the leucine-rich domain prevent activation of Ste11 and block nuclear accumulation and recruitment of Ste5. (A) Ste5Δ474-487 and Ste5L482/485A are defective in nuclear accumulation and plasma membrane recruitment. Indirect immunofluorescence of Ste5 mutants tagged with nine copies of the Myc epitope as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Strains were ste5Δ (EY1775) expressing either Ste5-Myc9 (pSKM19), Ste5Δ474-487-Myc9 (pYMW4), or Ste5L482/485A-Myc9 (pYMW37) from 2μ plasmids. %N.E. is the percentage of cells in which Ste5-Myc9 derivatives seemed to be excluded from the nucleus. Nuclear exclusion (indicated by the arrows) was defined as a reduced immunofluorescence signal in the nucleus compared with the surrounding cytoplasm. (B) Quantitation of FUS1-lacZ expression, G1 arrest, and mating in STE5, ste5Δ474-487, and ste5L482/485A strains. For all assays a MATa bar1Δ ste5Δ (EY1775) strain was transformed with CEN plasmids expressing Ste5 (pYBS138), Ste5Δ474-487(pYMW7), or Ste5L482/485A (pYMW39). β-Galactosidase activity was assessed in strains that were cotransformed with a 2μ FUS1-lacZ plasmid (pJB207). (C) Ste5Δ474-487 and Ste5L482/485A do not efficiently associate with Ste11. Ste11-Myc (pNC245) was immunoprecipitated with 9E10 (anti-Myc), and immune complexes were tested for the presence of Ste5-GST (pYMW77), Ste5Δ474-487-GST (pYMW49), Ste5L482/485A-GST (pYMW64), or vector control by using anti-GST antibody. Strains were grown in 2% galactose medium for 5 h to induce expression of Ste11-Myc. (D) Ste5Δ474-487 and Ste5L482/485A fail to positively regulate STE11-4, a hyperactive version of Ste11. Quantitation of FUS1-lacZ expression in STE11-4 ste5Δ (EYL1809) cells cotransformed with CEN (YCplac22), STE5 CEN (pYBS138), ste5Δ474-487 CEN (pYMW7), or ste5L482/485A CEN (pYMW39) and FUS1-lacZ 2 μ (pJB207). For B and D, cells were induced with α factor (50 nM) for 90 min.