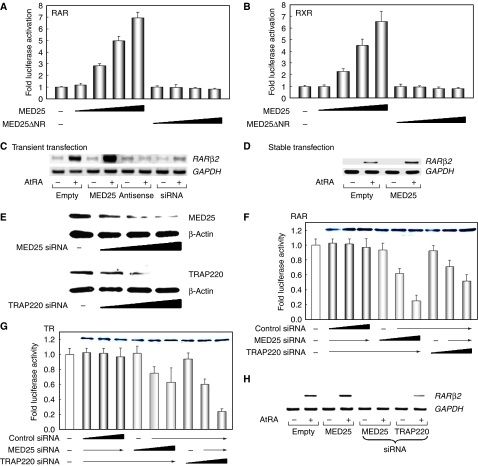
Figure 3.
MED25 is a coactivator of RAR as determined using overexpression (A–D) and reduced expression (E–H) conditions. (A, B) Effect of MED25 on the transcriptional activity of RAR and RXR. NIH3T3 cells were transfected with expression vectors for RAR (or RXR) and MED25 (or ΔNR), with RARE- or RXRE-tk-luciferase, in the absence or presence of 1 μM ligand (AtRA for RAR; 9-cis RA for RXR). Relative luciferase activity was determined by luciferase assay after normalizing to the observed β-galactosidase activity. The fold activation is a comparison between the luciferase activity in the presence and absence of ligand. The data shown are averages from three independent experiments. (C, D) Effect of MED25 on endogenous RARβ2 expression. (C) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with a MED25 sense or antisense expression vector and treated with MED25 siRNA. (D) MCF-7 cells stably expressing MED25 were selected by G-418 treatment. Total RNA was extracted from each cell and subjected to RT–PCR using primer pairs specific for the RARβ2 coding sequence. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (E–H) Downregulation of MED25 resulted in a significant and specific reduction in RAR activity. (E) Increasing amounts (0, 80, 160, and 240 pmol) of MED25 or TRAP220 siRNA were added to HeLa cells. The extent of knockdown was monitored by WB. β-Actin was used as an internal control. (F) HeLa cells were transfected with control, MED25, or TRAP220 siRNA (0, 40, 80, and 120 pmol) and the RARE-tk-luciferase reporter in the presence of 1 μM of AtRA. The level of endogenous RARα was determined by WB (inset). Luciferase activity was determined as described above. (G) The DR4-tk-luciferase reporter was used instead, and the level of TR is shown (inset). Each graph shows the average data obtained from three independent experiments. (H) The knockdown effect was analyzed by RT–PCR using primer pairs specific for the RARβ2 coding sequence.