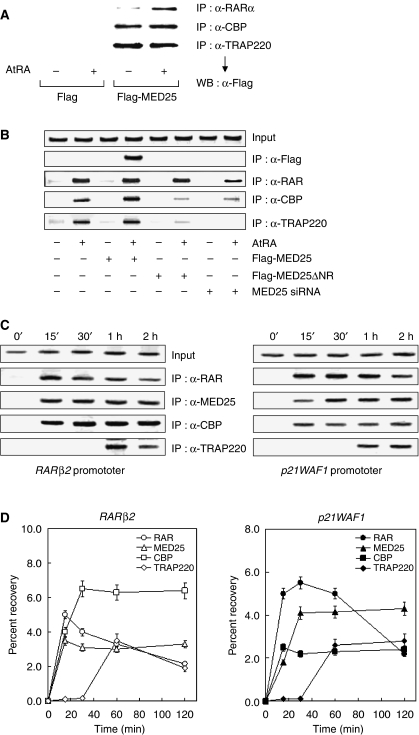
Figure 7.
Chromatin association of MED25 with RAR, CBP, and TRAP220. (A) Binding of MED25 to endogenous RAR, CBP, and TRAP220. HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-MED25 expression vector in the absence or presence of 2 μM AtRA. RAR and the indicated cofactors were immunoprecipitated from whole extracts of transfected cells using the indicated antibodies. MED25 was detected in precipitates by WB with anti-Flag antibody. (B) AtRA-dependent recruitment of MED25 and other RAR cofactors. HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-MED25 or MED25 ΔNR expression vector or MED25 siRNA and then treated with or without 2 μM AtRA for 2 h. Crosslinked chromatin was prepared and immunoprecipitated with the antibodies indicated on the right. The precipitates were subjected to PCR analysis using primer pairs spanning the human RARβ2 promoter. The control represents the PCR product obtained before IP. (C) Sequential recruitment of MED25 and other RAR cofactors. ChIP assays were performed as in Figure 7B, except that HeLa cells were treated with AtRA for varying lengths of time (shown above the lanes) and another RA-responsive promoter was included (p21WAF1). The primers used for the p21WAF1 promoter were obtained from Zeng et al (2002). The antibodies used are indicated on the right. (D) Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using the double-stranded DNA binding dye SYBR Green in an iCycler (Bio-Rad). All of the data (the average of three independent amplifications) represent the recovery of each DNA fragment relative to the total input DNA.