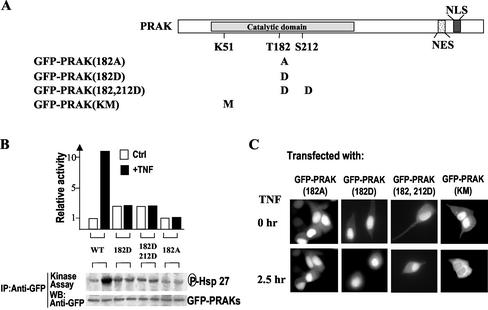
Figure 4.
Nuclear export of PRAK requires the regulatory phosphorylation site T182 but not kinase activity of PRAK. (A) A schematic primary structure of PRAK indicates the position of the catalytic domain and the motifs of NES and NLS. Mutations that altered the phosphorylation sites (T182, S212) or ATP pocket (K51) were shown under the structure. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vector of different GFP-PRAK mutants as indicated. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were treated with or without TNF for 2 h. The kinase activity of GFP-PRAK mutants was analyzed by immunokinase assay as in Figure 3C. (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vector of different GFP-PRAK mutants as indicated. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were treated with or without TNF for 2 h. The locations of GFP-PRAK were analyzed by fluorescent microscopy. TNF-induced nuclear export of GFP-PRAK was impaired by mutations on T182 site but not by a mutation in ATP pocket.