Figure 4.
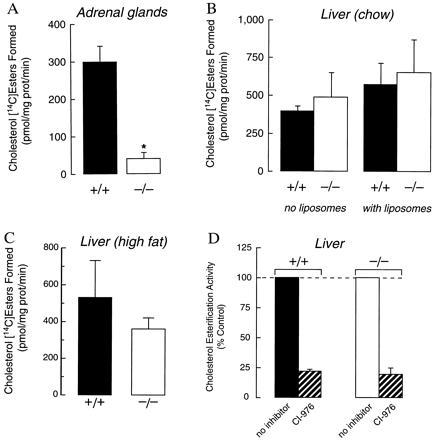
Cholesterol esterification activity in adrenal membranes and hepatic microsomes of wild-type and Acact−/− mice. (A) Adrenal membrane activity in female mice. Assays were performed with 100 μg of protein as described in Materials and Methods. Results are shown for three samples for each genotype; each sample contained pooled adrenals from two mice. Exogenous cholesterol (20 nmol) in the form of liposomes was added during the preincubation. ∗, P < 0.01 versus Acact+/+. (B) Hepatic membrane activity of female mice fed a chow diet. Assays were performed with 150 μg of protein in the presence or absence of 20 nmol of exogenous cholesterol provided as liposomes during preincubation (Acact+/+, n = 3; Acact−/−, n = 3). (C) Hepatic membrane activity of mice fed a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet. Assays were performed with 150 μg of protein without added cholesterol (Acact+/+, n = 3; Acact−/−, n = 3). P = 0.20 for the difference between means. (D) Effects of the ACAT inhibitor CI-976 (10 μg/ml) on cholesterol esterification activity of hepatic microsomes from chow-fed mice. Assays were performed after preincubation with exogenous cholesterol.
