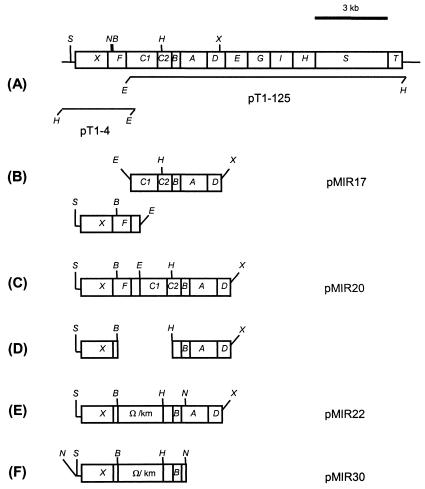
FIG. 2.
Construction of plasmid pMIR30 used for generation of mutant DOT-T1EΔtodC by allelic exchange. (A) Physical organization of the tod genes. (B) A ∼4.5-kb EcoRI/XcaI fragment of pT1-125, which carried genes todC1 to todD, was subcloned at the EcoRI/SmaI sites of pUC18NB-H, generating plasmid pMIR17. (C) The 1.8-kb SspI/EcoRI fragment of pT1-4, containing the todXF genes, was subcloned at the EcoRI site of pMIR17 to obtain plasmid pMIR20 (the unique NotI site present in the SspI/EcoRI fragment was removed before cloning). (D) Most of the 3′ half of todF, the entire todC1 gene, and the 5′ end of todC2 were removed from pMIR20 as a 2.2-kb BamHI/HindIII fragment. (E) Insertion of a 2.2-kb Ω/Km cassette (4) to obtain pMIR22. (F) pMIR30 was obtained as a result of subcloning in pKNG101 of the NotI fragment of pMIR22, which contained the insertional deletion todF′ΔtodC1::km::′todC2. Restriction sites are indicated as follows: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; N, NotI; S, SspI; X, XcaI. Ω/km, interposon encoding kanamycin resistance.