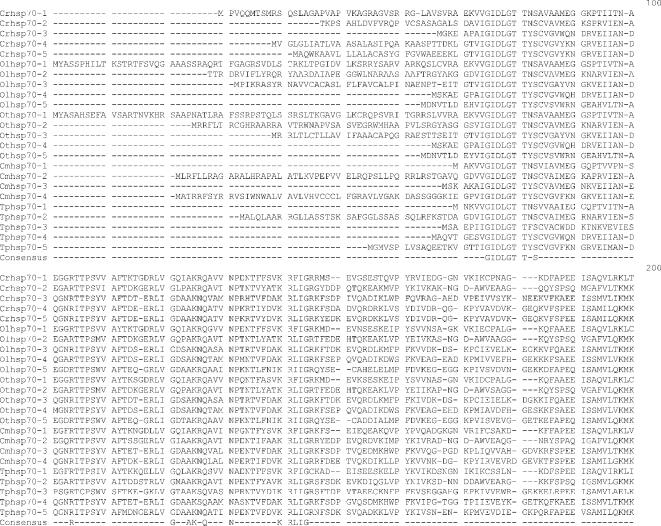
Fig 1.
Alignment of heat shock 70 proteins (HSP70s) amino acid sequences from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr), Ostreococcus lucimarinus (Ol), Ostreococcus tauri (Ot), Cyandioschyzon merolae (Cm), and Thalassiosira pseudonana (Tp). Amino acid residues 1–70 in the alignment include the variable N-terminal region. This region is absent in cytoplasmically localized HSP70s and contains the transit sequences for mitochondrion (MT), chloroplast (CP), and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) HSP70s. The much more highly conserved adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) domain includes residues 70–475. This region displays considerable sequence conservation but also has regions of insertion or deletion of 1 to a few residues. The peptide-binding domain (residues 490–645) is extremely well conserved. The variable C-terminal region (645–760) is absent in some proteins and highly variable in others, and its function is not well established. It also contains ER and cytoplasmic consensus sequences. The cytoplasmic consensus sequence GP(T/K)(V/I)EEVD at residues 762–769 is in bold. The ER consensus sequence HDEL at residues 765–769 is underlined