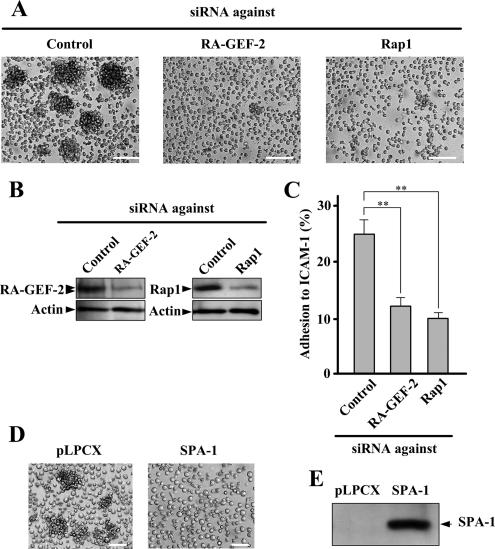
Figure 2.
The involvement of RA-GEF-2 and Rap1 in M-Ras[Q71L]–induced cellular aggregation. (A) Inhibition of M-Ras[Q71L]–induced cellular aggregation by down-regulation of RA-GEF-2 and Rap1. BAF/hLFA-1/M-Ras[Q71L] cells transfected with siRNAs against control (Control), RA-GEF-2, and Rap1 were observed by microscopy. Each bar, 100 μm. (B) siRNA-induced reduction of protein expression. After siRNA treatment, protein extracts were prepared and used for immunoblotting by anti-RA-GEF-2 and Rap1 antibodies. (C) Inhibition of M-Ras[Q71L]–induced adhesion to ICAM-1 by down-regulation of RA-GEF-2 and Rap1. BAF/hLFA-1/M-Ras[Q71L] cells transfected with siRNAs against control (Control), RA-GEF-2, and Rap1 were examined for adhesion to ICAM-1. Cells bound to ICAM-1 were detected by fluorescence analyzer. Bars represent the average and SE of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. **p < 0.01. (D) Inhibition of M-Ras[Q71L]–induced cellular aggregation by SPA-1. SPA-1 was not expressed (pLPCX) or expressed (SPA-1) in BAF/hLFA-1/M-Ras[Q71L] cells, and cells were observed by microscopy. Each bar, 50 μm. (E) The expression of SPA-1. Protein extracts prepared from cells shown in D were used to confirm the expression of SPA-1 by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibody.