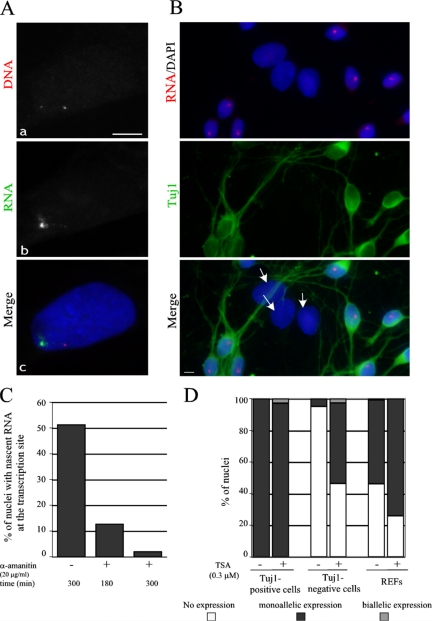
Figure 2.
Monoallelic expression at the Bsr locus. (A) A representative REF nucleus simultaneously hybridized with the Cy3-labeled DNA probes (a) and the Oregon green–labeled intronic probe (b) to detect nascent transcripts. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. In some nuclei, very faint RNA signals around the second silent Bsr allele can sometimes be detected, probably due to the fact that the intronic probe can also hybridize to the DNA (not shown). Bar, 5 μm. (B) Monoallelic expression of Bsr is mainly restricted to neurons in E.17 primary rat hypothalamus cells. The panel shows a representative field of cultured primary hypothalamic neurons hybridized with a Cy3-labeled intronic probe (only a single nascent RNA signal is detected per nucleus) and stained by a monoclonal Tuj1 antibody to reveal neurons. Note that Tuj1-negative cells with larger nuclei (white arrows), most of which are astrocytes, do not express the Bsr gene. (C) Transcription of the Bsr gene is sensitive to α-amanitin. The percentage of nuclei with nascent RNAs at the transcription site (detected by the Cy3-labeled intronic probe) were scored in the control cells (−) and in the cells treated (+) by α-amanitin for 180 and 300 min (a minimum of 200 nuclei were analyzed). (D) Monoallelic expression at the Bsr locus is resistant to TSA treatment. Primary cultured hypothamic neurons or REFs were treated by TSA as indicated and the percentage of nuclei with none, one, or two transcription sites are indicated (a minimum of 200 nuclei were scored).