Fig. 6. Activation of JNK by bFGF in astrocytes.
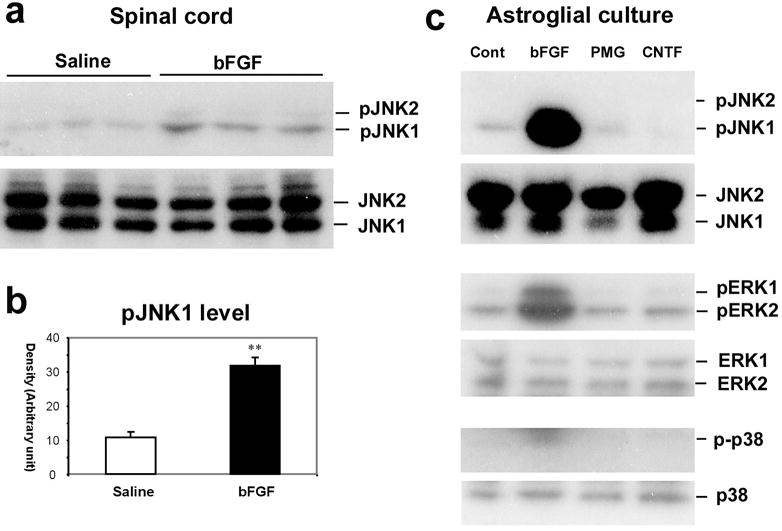
(a) Upper panel: Western blotting in the upper panel reveals an increase in pJNK1 levels in the spinal dorsal horn after bFGF infusion intrathecally via an osmotic pump (10 ng μl−1h−1) for one week. The spinal tissues were collected on day 8 after final behavioral testing (see Fig. 5). Note that only pJNK1 is expressed in the spinal cord. Lower panel: total concentration of JNK does not change after bFGF infusion. (b) Density of pJNK1 bands in (a), normalized to JNK1 loading control. **, P<0.01 compared to saline control. (c) Western blotting shows that bFGF induces pJNK1, pERK1 and pERK2 in astrocytic cultures. By contrast, plasminogen (PMG) and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) do not activate JNK. p-p38 levels are barely detected in astroglial cultures following all the reagents. Astroglial cultures were prepared from brains of neonatal rats and maintained for 2–3 weeks. Cultures were stimulated with bFGF, PMG and CNTF (each at 100 ng ml−1) for 2 hours.
