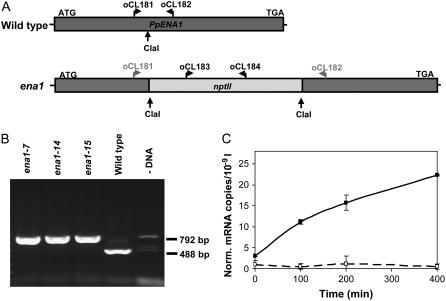
Figure 3.
Generating PpENA1 knockouts by homologous recombination. A, cDNA clone of PpENA1 was restriction enzyme digested at a unique ClaI site and the nptII gene inserted to generate a knockout cassette. B, The transformants were screened by PCR on genomic DNA using a mix of primers specific to PpENA1 (oCL181, oCL182) and nptII (oCL183, oCL184). A 488-bp band is expected in the wild type and a 792-bp band in the transformants where the PpENA1 gene has been replaced by the knockout cassette (ena1). Although all four primers anneal to the PpENA1 knockout cassette, the short fragment will be favored during the PCR. If the selective cassette is inserted in the genome, without replacing the PpENA1 gene, both the 488- and 792-bp PCR fragments will be present. C, PpENA1 mRNA levels. To ensure that PpENA1 was not expressed in the ena1 lines, mixed protonemata and gametophytes from wild type (black line) and ena1 (stippled line) were exposed to 100 mm NaCl and tissue harvested at different time points used for qRT-PCR. PpENA1 expression was normalized against four control genes (see “Materials and Methods”).