Figure 4.
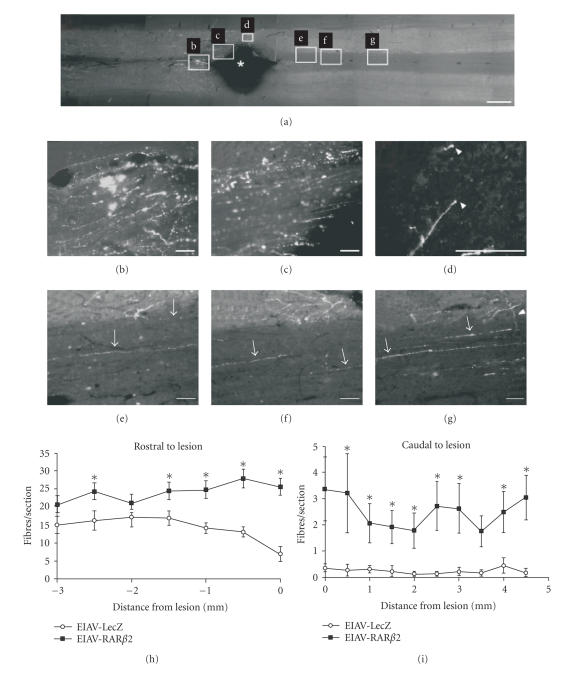
Transfection of RARβ induces regeneration of corticospinal axons in vivo. (a) Longitudinal sections of the adult rat spinal cord were traced with BDA to determine fibre regeneration in the corticospinal tract; overview of the lesion site in an animal injected with the RARβ2 expressing construct (EIAV-RARβ2, Rostral: left). (b) Animals with RARβ2-transfected cells displayed less fiber degeneration than control rats. (c) Labeled axons were detected up to the edge of the lesion, (d) at the distal edge of the lesion, and (e–g) at various distances caudal to the lesion. Growth cone-like endings were detected at the tips of some axons (white arrowheads in d). Axons appear to send collaterals (white arrowhead in g) from white matter to grey matter. (Scale bars in (a): 1mm, in (b–g): 100μ m.) (h–i) Quantification of BDA-labeled fibres in the corticospinal tract after spinal cord lesion. EIAV-RARβ2-treated animals displayed increased fiber numbers rostral and caudal to the lesion compared to control animals (P < .05, two-way ANOVA) (source: [100]).